Lecture 19 Flashcards
What are these structures?
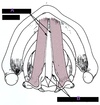
A. membranous glottis
B. Cartilaginous glottis
Glottal Configurations

A Quiet Breathing
B. Forced inhalation
C. Normal phonation
D. whisper
Cover-Body Theory
Introduced by?
Parts
Idea to remember?
Hirano, 1974
cover: squamous epithelium superficial layer lamina propria
transition: intermediate layer and deep layer of lamina propria = vocal ligament
body: thyrovocalis portion of thyroarytenoid muscle
**for vocal fold vibration it is important to keep in mind that the body and the cover will have different vibratory characteristics
What part of the larynx does CN V innervate?
(trigeminal nerve)
anterior belly of the digastricus, mylohoid
What part of the layrnx does CN VII innervate?
(facial nerve)
posterior belly of the digastricus, stylohoid
What does CN XII innervate?
(hypoglossal nerve)
geniogyoid, thyrohyoid
What do spinal vervs C1-C3 innervate?
sternohyoid, omohyoid and sternothyroid
What are CN X and XI branches of and where do they provide sensory innervation?
braches of ISLN (internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve)
sensory innervatio to mucous membrans of vestibule(additus), pharynx, base of tongue, soft palate, larynx (down tot he vocal folds) and epiglottis
Where does teh ISLN enter through?
the hyothyroid membrane
What does the ESLN do?
CT motor control
What does RLN do?
all intrinsic motor control except CT
Label
A
B
C

A right recurrent laryngeal nerve
B. Superior laryngeal nerve
C. Left recurrent Laryngeal nerve
What is the myloelastic aerodynamic theory?
Muscle + elasticity + airflow/pressure = vocal fold vibration
–Vocal folds are adducted by coordinated contraction of LCA and IA that places folds at midline
– –Pressure builds up below the vocal folds relative to above the vocal folds
– –Pressure becomes sufficient to overcome the medial compression of the folds and blows them apart as air flows through the folds.
– –Resultant aerodynamic effects and elastic recoil forces of the vocal folds returns the folds to the midline
What is opening phase?
percentage of time the vocal folds are in the act of opening during one vocal cycle - 50%
What is closing phase?
equal percentage of time the vocal folds are in the act of closing during one vocal cycle
37%

