1/20/15 Flashcards
What is the definition of myelophthisis? What are the morphological characteristics of RBCs in this condition?
replacement of the bone marrow by metastatic carcinoma, fibrosis or granulomatous disease. RBCs look like tear-drops
What are the etiologies of aplastic anemia?
idiopathic viral infections (unknown hepatitis virus, HIV, EBV, CMV) drugs/chemo (chloramphenicol, benzene, sulfonamides, radiation) defects in telomerase gene defects in DNA repair (Fanconi anemia)
What are the signs of Fanconi anemia?
pancytopenia/aplastic anemia short stature hypoplastic thumbs hypo pigmented skin hypogonadism microcephaly
In what organs does fetal hematopoiesis take place?
Young Liver Synthesizes Blood Yolk sac -> liver -> spleen -> bone marrow

Poliomyelitis or Werdnig-Hoffman syndrome
Destruction of the anterior horns. LMN lesions only

Multiple sclerosis
Random, asymmetric demyelination of white matter

ALS
Lateral corticospinal tract and anterior horn degeneration. UMN and LMN signs

Tabes dorsalis

Syringomyelia
seen in Chiari I malformations
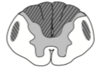
Vitamin B12 defciency
Subacute, combined degeneration of lateral corticospinal tract and posterior column
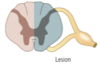
Brown-Sequard syndrome
What is Parinaud syndrome?
paralysis of vertical conjugate gaze due to a lesion in the superior colliculus, possibly from a tumor of the pineal gland
What are the three vagus nerve nuclei? what is their function?
Nucleus solitarius - visceral sensory information (taste, baroreceptors, gut distension)
Nucleus Ambiguus - motor innervation to pharynx, larynx and upper esophagus (swallowing, palate elevation)
Dorsal motor nucleus - parasympathetic fibers to the heart, lungs and upper GI
What are the afferent and efferent nerves in the following reflexes? corneal, jaw-jerk, lacrimation, pupillary, gag
Corneal reflex: afferent = V1, efferent = CN VII
Jaw-jerk reflex: afferent = V3, efferent = V3
lacrimation: afferent = V1, efferent = VII
Pupillary: afferent = CN II, efferent = CN III
Gag: afferent = glossopharyngeal; efferent = vagus

