4⼀PULMONARY/ALLERGY/ENT Flashcards
(249 cards)
What would you expect PFT for a patient with Asthma to be?
NORMAL PFT
but
[FEV1⬇︎ ≥20% (on methacholine challenge)]
“Either [BD → ⇪EVC] or [MC → ⬇︎EV]”

What are the recommendations regarding Influenza vaccine and [patients with “egg” allergy] ? (3)
pt s/p…
- [urticarial (egg rxn)]? → give [IM dead influenza vaccine]
- [SEVERE (egg rxn)]? → give [IM dead influenza vaccine] in healthcare setting under supervision
- [SEVERE (VACCINE rxn)]? → [INFLUENZA VACCINE❌CONTRAINDICATED]

Management for Asthma Exacerbation (3)

PIR

1st: [PAWSS respiratory failure?]
2nd: [Initial tx(SMC vs Mechanical Ventilation)
3rd: [Reassess q2-4h]
Whats the best medication for Awake Intubation induction?
_________________
why? (6)
Ketamine
_________________
“has a BAD RUP”
provides [BronchoDilation | Analgesia | Dissociative amnesia]
+
maintains [Respiratory drive | Upper airway tone | Protective reflex]
How is smoking/secondhand smoking a/w Chronic Sinusitis?
_________________
Name 3 other major causes of Chronic Sinusitis
cigarette smoke damage cilia ➜ ⬇︎mucus flow throughout the sinus ➜ chronic sinusitis
_________________
poorly treated acute sinusitis / [structural abnormality (nasal septum/palate)] / rhinitis
SMHHsx = [Snotty purulent nasal discharge/Maxillary facial pain/HA/Hot>39C]
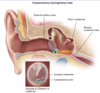
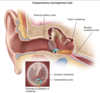
Most epistaxis originate from the ⬜ in the ⬜
How do you manage this? -4
[Kisselbach Plexus] ; [ANTERIOR Nasal Septum]
________________
- try each tx until epistaxis resolved*
1st: Nostril pinching
2nd: [Topical Vasoconstrictor]
3rd: [Cautery (silver nitrate vs electrical)]
4th: [ANT nasal packing with bacitracin-sponge]

Tx for [Bacterial Aspiration PNA] -3
look for infiltrate in dependent portion of the lung
βMα
_________________
[CefTriaxone + Azithromycin](community acquired PNA)
+
[anaerobic abx if empyema or lung abscess present]

treatment regimen for GASP? -2
________________
What are the alternatives if a patient is allergic? -3
________________
Why is it important to treat GASP?
GASP = [Group A Strep Pyogenes]
[PO PCN VK]10d or [PO amoxicillin]10d
________________
allergy mild = Cephalosporin
allergy anaphylaxis = Azithromycin | Clindamycin
________________
prevention of Rheumatic Fever

What’s the most common cause of hemoptysis?
[Bronchial infxns (Bronchitis / Bronchiectasis)]

What are the most common organisms to cause Sinus infection (Rhinosinusitis)? - 3
________________
Tx?
Strep Pneumo > HFlu nontypeable > moraxella
________________
Tx = Amoxicillin/clavulanate
[Haemophilus Influenzae] Tx (5)
HaEMOPhilus
[FAT MC]
[Fluroquinolone vs. Ampicillin vs. Tetracycline vs. Macrolide(NOT ERYTHRO) vs. Ceftriaxone]
🄰. [Daily Cough with mucopurulent sputum and [Recurrent multiLobar PNA] likely indicates what dx?
________________
🄱 . How does this disease cause hemoptysis?
_________________
🄲. Explain why [Recurrent single lobe PNA] has a different workup
🄰 . Bronchiectasis
________________
🄱.
💥[multilobar poor ciliary clearance(2/2 Kartagener | CF | ABPA, etc) ] → *multilobar *bronchial wall infection ➜
💥[inflammatory bronchial wall thickening and permanent airway dilation]+ inflammation predisposes to repeat infections
💥➜ more bronchial wall thickening and dilation= [cycle of bronchial airway dilation + bronchial wall thickening+ bronchial wall inflammation]
💥➜chronic [bronchial wall inflammation] ➜ rupture of [bronchial wall superficial blood vessels] ➜ hemoptysis

c.
Focal bronchiectasis (involvement of single lobe/segment only) indicates airway blockage (malignancy/foreign body) ⼀ = Dx/Tx = FLEX bronchoscopy (since HRCT may not reveal/remove the obstructing lesion)
so…
🧠pts with [persistent Recurrent PNA] in:
[single lobe → 🔬FLEX BRONCHOSCOPY]
vs
[Multi lobe → 🔬HRCT]
Name the Causes of ARDS (10)
ARDS
A= Aspiration vs. [Acute Pancreatitis] vs. [Air Fluid Embolus (amniotic)]
R= Radiation
D= Drugs vs. DIC vs. Drowning
S= Sepsis vs. Smoking vs. Shock
ARDS is a restrictive pattern that –> [⬇︎Lung Compliance], [Group 3Pulm HTN] and impaired gas exchange
What are the 3 criteria for COPD Exacerbation
Co-P-D
[Cough ⇪ with SPUTUM ∆]
[Pulmonic WHEEZING BL]
[Dyspnea ( ➜respiratory acidosis)]
Out of the Tx for COPD Exacerbation
Which improves survival?
________________
Which ⬇︎future events?
“I’m having COPD Exacerbation! Give me DOPA! (but not really)”
[O2 PRN via BiPAP (goal: 90-94% O2 Sat)]
________________
Abx (Azithro-⬇︎future events or Levoflox or Doxy)
Tx for COPD Exacerbation-4
“I’m having COPD Exacerbation! Give me DOPA! (but not really)”
- Duoneb (albuterol + ipratropium)
- O2 PRN via BiPAP (goal: 90-94% O2 Sat)
- [Prednisone 40 mg qd x 5]
- Abx (Azithro-⬇︎future events or Levoflox or Doxy)
how is [PPSV 23 (Pneumococcal PolySaccharide Vaccine)] used in peds? (3)
PPSV23 in kids is used for peds at high risk for pneumococcal disease
- [Sickle Cell Anemia\Asplenia]
- Cardiac ❌
- cochlear implants
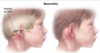
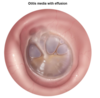
diagnostic criteria for Acute Otitis Media -2
________________
Which organisms cause AOM? -3
BULGING TM + [Middle Ear effusion with TM inflammation (fever/otalgia/erythema)]
________________
STREP PNEUMO = [HFLU NONTYPEABLE**] >> moraxella
________________
** also causes otitis conjunctivitis syndrome

Prophylactic abx tx and tympanostomy tube ⬇︎ [recurrent AOM],
and are recommended for which 4 patient groups?
[≥ 3 AOM in 6 mo] or
[≥4 AOM in 12 mo] or
[craniofacial DO] or
[neurodevelopmental DO = speech/hearing ❌]

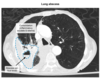
How long does it take Malignant [Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodules] to double in size?
________________
How does this affect diagnostics?

1 month - 1 year

________________
Pt with stable [Solitary Pulm Coin Nodule] > 1 year = NO CA!
Pt with hemoptysis comes in with [Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodule] on CXR
What are the 3 [preDiagnostic Mgmt] steps for SPN?

A: LOCATE PREVIOUS CXR ≥ 1y old!
_________________
b: If SPN unchanged = NO CA
C: If [(SPN ∆) OR (NO PRIOR CXR)] ➜ [Diagnostic Mgmt] (image)

Coin lesions = 80% chance malignancy
List 5 characteristics of [solitary pulmonary coin nodules] that help to determine their Malignancy & workup

Smoking hx | Location | Age | Border || size
-Smoking Hx
-Location: Endobronchial proximal extension/Local invasion/Satellite Nodules
-Age
-Border: : Spiculated / Retracted from surrounding tissue / irregular
-size: {≥8mm}

After the [SPN 3-step prediagnostic mgmt]
How do you workup [Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodule]?

Round, < 3mm, no LAD

[Solitary Pulmonary Coin Nodule] DDx -5

- CA(hamartoma/metastasis/primary)
- Infectious [granulomatous/fungal (blasto,histo)]
- Pneumoconiosis
- Vasculitis
- Scar