7 ⼀ENDOCRINE/OPHTHO Flashcards
(350 cards)
how are pregnant patients screened for hyperthyroidism? (3)
torn
TSH
(low TSH) ➜ [free T4]
(normal [free T4]) ➜ [Total T3]
use trimester-specific norms
management? (2)

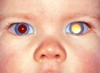
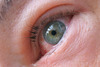
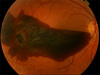
eye shield
+
[hospital admit (strict bed rest + 30° bed + serial intraocular pressures+ [prevent rebleeding and intraocular HTN → vision loss])]
HYPHEMA
Stress Hyperglycemia occurs when ⬜. This presents very similarly to ⬜
_________________
how do you differentiate the two? (2)
Stress Hyperglycemia is a/w ⇪ morbiditiy
[STRESS (severe illness > 39C)] ➜ [CortisolGlucocorticoid] secretion➜ ⇪ Insulin resistance ➜ hyperglycemia ;
DKA
_________________
DKA has [hgbA1C ≥6.5%] +[“FUDGe” DM classic s/s]
patient newly diagnosed with Papillary Thyroid Cancer
What’s 1st step after this?
_________________
What are the treatments? (2)
[Neck & Cervical lymph node US for initial staging]
_________________
- [< 1 cm = lobectomy]
- [TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY if: ≥1cm | extension outside thyroid | distant metz | hx head/neck radiation exposure]
Which antiDM are a/w weight gain? (3)
Insulin
[Thiazolidinediones (pioglitazone)]
Sulfonylurea
“Insulin Tops Scales”
What is Euthyroid Sick Syndrome? (4)
_________________
mgmt? (3)
⭐acute illness ➜ [⬇︎ peripheral conversion of T4➜ T3] → forces peripheral T4 to be converted to ®T3 instead
⭐but causes no other change to the thyroid →[nml TSH, nml T4 ]
with
⭐[low T3io\normal TSH and normal T4]
and
⭐[HIGH ®T3io\normal TSH and normal T4]
[ ✔︎TSH, ✔︎T4, , ⬇︎T3, ⇪®T3 ] = Euthyroid Sick Syndrome
should resolve once acute illness is resolved
_________________
Repeat Thyroid Function Test after acute illness is resolved –(if persist)–> give [Liothyronine T3] supplement
What is [reverse ®T3]?
_________________
what is it used for?
rT3 = [inactive metabolite of unconverted T4]
_________________
[rT3] Differentiates …
Euthyroid Sick Syndrome (illness ⬇︎ peripheral conversion of T4 ➜ T3 = [⬇︎T3] but [⇪ rT3 (from INC unconverted T4)])
_________from________
central hypOthyroidism (low TSH ➜ ⬇︎T4 ➜ [⬇︎T3] AND [⬇︎rT3])
How do you workup a patient with suspected [central hypOpituitarism] (5)

patients with [classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia] require prompt therapy with ⬜ and chronic tx with ⬜
Why ? (3)
[high dose hydrocortisone] ; glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement
_________________
avoid adrenal crisis by maintaining BP / growth/ suppress adrenal androgens
classic CAH = 21hydroxylase deficiency CAH

Recite the Adrenal Gland blueprint for
Zona Glomerulosa (13)
*

Recite the Adrenal Gland blueprint for
Zona Fasciculata -7

Recite the Adrenal Gland blueprint for
Zona Reticularis-6

The most common enzyme deficiency for [Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia] is
⬜
________________
cp?-3
21 hydroxylase
[(complete=CLASSIC CAH (C)] | [(reduced=NONClassic CAH (NC)]
🅶
▶C[⬇︎AldosteroneMineralocorticoid] → [Salt Wasting( losing Na+ / gaining K+)] → hypOtension + vomiting
🅵
▶C[⬇︎CortisolGlucocorticoid]
🆁
▶NC & C[⇪Testosterone] ← [⇪ 17HydroxyProgesterone]
= Virilization = [Ambiguous genitalia in females] + (acne, premature adrenarche/pubarche)

MC=MineraloCorticoid/GC=GlucoCorticoid
The 2nd most common enzyme deficiency for [Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia] is
⬜
________________
cp?-5
11βhydroxylase
🅶
▶ [⇪ 11DOCSMC] = weak Mineralocorticoid → Salt Retention → Fluid Retention = HTN
▶[⬇︎AldosteroneMineralocorticoid]
🅵
▶[⇪11dcGC]
▶[⬇︎CortisolGlucocorticoid]
🆁
▶[⇪ ⇪Testosterone] ← [⇪⇪ 17HydroxyProgesterone] ← {[⇪11DOCSMC]🅶 & [⇪11dcGC]🅵}
= Virilization = [Ambiguous genitalia in females] + (acne, premature adrenarche/pubarche)
[11dc =11deoxycortisol] | [11DOCS =11DeOxyCorticoSterone] | MC=MineraloCorticoid/GC=GlucoCorticoid

The least common enzyme deficiency for [Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia] is
⬜
________________
cp?-2
17 αhydroxylase
🅶
▶[⇪ ⇪ AldosteroneMineralocorticoid] ← [⇪⇪ 11DOCSMC]
= Salt Retention → Fluid Retention = HTN
🅵
▶[⬇︎CortisolGlucocorticoid]
🆁
▶[⬇︎Testosterone]
= ALL PATIENTS PHENOTYPICALLY FEMALE
[11dc =11deoxycortisol] | [11DOCS =11DeOxyCorticoSterone] | MC=MineraloCorticoid/GC=GlucoCorticoid

The most common enzyme deficiency for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia is ⬜
Which lab value is diagnostic for this deficiency?
21 hydroxylase (complete = classic CAH | reduced=nonClassic CAH)
⬆︎17 HydroxyPROGESTERONE

What benefits does maintaining Tight Glucose Control in DM pts give?
⬇︎ microvascular complications (retinopathy/nephropathy)
What are all the functions of [CortisolGlucocorticoid] - 6
⇪BIG ⬇︎FIB
- ⇪ Blood pressure (⬆︎a1 receptors)
- ⇪Insulin resistance –> DM
- ⇪Gluconeogenesis
_________________ - ⬇︎Fibroblast –> striae
- ⬇︎Immune system (WHITE)
- ⬇︎Bone formation by ⬇︎osteoBlast
what is Apathetic Thyrotoxicosis ? (4)
- [atypical elderly HYPERthyroidism] =
- [APATHY (lack of enthusiasm/interest), mimics DEPRESSION, lethargy, confusion, wt loss]
- (misdiagnosed as depression or dementia),
- likely NO thyromegaly
S/S of hypOthyroidism is mostly opposite of Hyperthyroidism sx
What are 9 symptoms specific to only hypOthyroidism?
Mostly opposite of TT Feels ARCHED but specifically causes {med}3…
menorrhagia
macroglossia
myalgia/arthralgia
[edema ([Myxedema nonpitting] / pedal)]
[eval labs (HLD, Macrocytosis & hypOnatremia in elderly)]
[eerie (HOARSE) voice]
diastolic HF
depression
dry coarse skin
BOTH HAVE FATIGUE AND HTN
Clinical definition of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) -2
[metabolic acidosis (HCO3<15 or pH<7.3)]
in the setting of [hyperglycemia > 200]
how do you manage HHONKS-6?
[HHONKS (Hyperglycemia HyperOsmolar NON Ketone State)]
FIPAAR control
-
Fluid control : (NS) < [Blood Sodium 135] < (1/2 NS)
_________________ -
Insulin control:
🍭[Continuous infusion until BG 200]]
🍭➜ [when BG ≤ 200 ⬇︎ infusion and add dextrose5%]
🍭➜ [on G.A.P.E.Resolution = start (subQ mealtime + basal insulin)] ➜ DC insulin infusion 2h later]
_________________ -
Potassium control: [✳]
_________________ -
Acid control: give HCO3 for [pH< 6.9 or HCO3< 15]
_________________ -
ANION GAP CONTROL: [correct to 10-14]
_________________ -
G.A.P.E.RESOLUTION = {[Glucose< 200] + [Anion Gap 10-14] + [pH>6.9 and HCO3 ≥15] + [Eating tolerated → ICU admitted]}
_________________
(monitor phosphate and Ca+ also)
[✳] : {serum K+: [(hold insulin) < –3.3–(give IV K+)– 5.2–> ✔︎]}
how do you manage DKA-6?
DKA:Diabetic Ketoacidosis
FIPAAR control
-
Fluid control : (NS) < [Blood Sodium 135] < (1/2 NS)
_________________ -
Insulin control:
🍭[Continuous infusion until BG 200]]
🍭➜ [when BG ≤ 200 ⬇︎ infusion and add dextrose5%]
🍭➜ [on G.A.P.E.Resolution = start (subQ mealtime + basal insulin)] ➜ DC insulin infusion 2h later]
_________________ -
Potassium control: [✳]
_________________ -
Acid control: give HCO3 for [pH< 6.9 or HCO3< 15]
_________________ -
ANION GAP CONTROL: [correct to 10-14]
_________________ -
G.A.P.E.RESOLUTION = {[Glucose< 200] + [Anion Gap 10-14] + [pH>6.9 and HCO3 ≥15] + [Eating tolerated → ICU admitted]}
_________________
(monitor phosphate and Ca+ also)
[✳] : {serum K+: [(hold insulin) < –3.3–(give IV K+)– 5.2–> ✔︎]}
[HHONKS (Hyperglycemia HyperOsmolar NON Ketonic State)**] is a complication of DM
What Blood Glucose precipitates this?
Blood Glucose > 600