6. Excitable Cells: Neural Communication Flashcards
(270 cards)
What are the two main nervous systems?
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
What structures make up the CNS?
- Brain
- Spinal cord
What structures make up the PNS?
All neuronal elements outside the brain and sponal cord:
- Cranial and spinal nerves -> Made of sensory and motor nerves
- Associated ganglia
- Supporting cells (e.g. Schwann cells)
Are sensory peripheral nerves divided into autonomic/somatic, parasympathetic/sympathetic, etc.?
They are sometimes divided into somatic and visceral afferent fibres, but CHECK THIS.
Draw a diagram to show the divisions of the nervous system.

What is the embryological origin of the central and peripheral nervous systems?
- CNS -> Neural tube
- PNS -> Neural crest

Describe the process by which peripheral nervous system cells develop (in terms of embryology).
They undergo:
- Specification
- Migration
- Differentiation
- Functional specification

What are the two divisions of the sensory division of the nervous system?
- Somatic sensory
- Consciously perceived
- Touch, pain, hearing, etc.
- Visceral sensory
- Not consciously perceived
- Stretch, chemical changes, taste, etc.
What are the two types of peripheral neurons?

Draw the structure of a reflex arc.

What are ganglia?
Egg-shaped structures containing cell bodies of neurons and glial cells supported by connective tissue.
i.e. It is where the cell bodies of neurons are.
What are unipolar, bipolar and multipolar neurons? Where is each found?
This essentially refers to the number of processes (e.g. axons) that come out of the cell body:
- Unipolar -> Sensory neurons with cell bodies in spinal and cranial nerve ganglia.
- Bipolar neurons -> Relatively rare. They are sensory neurons found in olfactory epithelium, the retina of the eye, and ganglia of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
- Multipolar neurons -> Most common. They are located in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and in autonomic ganglia.

Where do sensory neurons have ganglia?
Near the spinal cord -> These are called DORSAL ROOT GANGLIA
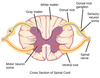
What is found in dorsal root ganglia?
The cell bodies of sensory neurons.
Where do sensory neurons usually terminate?
At interneurons of the CNS.
What are some different categories of sensory neuron receptors?
- Thermoreceptors – Respond to changes in temperature
- Photoreceptors – React to light
- Chemoreceptors – Respond to chemicals
- Mechanoceptors – Respond to pressure, touch vibrations
- Nociceptors – Respond to pain
Where are sensory receptors found?
They are found at the ends of sensory neurons.
Give some examples of sensory nerve endings and what they detect. [IMPORTANT]
- Meissner corpuscle -> Fine touch
- Merkel disc -> Touch
- Pacinian corpuscle -> Coarse touch, Pressure, Vibration
- Free nerve endings -> Heat, Pain
- Ruffini endings -> Stretch
Remember:
- Meissner sounds smooth so it detects smooth touch, while Merkel sounds rough so it detects coarser touch
- ViP STaR = Vibration is detected by Pacinian corpuscles, while Stretch and Temperature are detected by Ruffini endings
- Free nerve endings detect heat and pain
What stimulus do Meissner corpuscles detect?
Fine touch
What stimulus do Pacinian corpuscles detect?
Coarse touch, Vibration, Pressure
What stimulus do free nerve endings detect?
Pain, Heat, Touch
What stimulus do Ruffini’s corpuscles detect?
Stretch
What stimulus do Merkel’s disks detect?
Touch
Draw the positions and appearance of different sensory nerve endings near the skin.
Remember: The two M’s are in the epidermis along with the free nerve endings, while the rest are in the dermis.





























































