The Spinal Cord Flashcards
What are the general features of the spinal cord?
- Continuous with the brain
- Mediates spinal reflexes
- Site for nervous integration = contains synapses
- Provides pathways to and from the brain
What are the protections and coverings of the spinal cord?
- Vertebral canal (also called the spinal canal)
- Meninges (3 layers of connective tissue)
- Cerebrospinal fluid

What are the different meninges and spaces of the spinal cord pictured?

- Epidural space: outermost space made up of adipose tissue
- Dura mater: tough connective tissue
- Subdural space: in between dura mater and arachnoid membrane
- Arachnoid membrane: connective tissue like spider webs
- Subarachnoid space: innermost space
-
Pia mater: thin membrane that covers surface of spinal cord and holds blood vessels to cord
- denticulate ligaments: thin ligaments extend outward to anchor pia mater to spinal canal
- filum terminale: anchors the end of the spinal cord to the sacrum

What are the features of the external anatomy o the spinal cord pictured?

- Cylindrical shape
- Flattened Anterior-Posterior diameter
- Length of spinal cord: from Foramen magnum to L-2
- Differential growth: cord is different sizes
- Cervical enlargement b/c these nerve innervate the upper limbs
- Lumbar enlargement b/c these nerves innervate the lower limbs
- Conus medullaris: where the spinal cord ends
- Filum terminale: connects end of spinal cord to sacrum
- Cauda equina: collection of nerves from end of spinal cord to the end of the verterbral canal
- Functional segments: different segments of nerves service different regions of the body
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves

What are the features of the internal anatomy of the spinal cord pictured?

Gray Matter (non-myelinated)
- nuclei
- horns
→dorsal - sensory
→ventral - motor
→lateral - autonomic
White Matter (myelinated)
Gray Commissure
Central Canal
-contains cerebrospinal fluid

What are the different spinal nerve roots pictured?

Dorsal root ganglion – cell bodies of sensory neurons
Dorsal root – axons of sensory neurons
Ventral root – axons of motor neurons

What are the features of the white matter pictured?

Columns - names of white matter by location
-Dorsal, lateral, ventral
Tracts - relay info in CNS to/from brain
- ascending
- descending

What are the essential functions of the spinal cord?
- Convey impulses between periphery and brain
- Provide integrating center for spinal reflexes
What is a reflex?
Reflexes are
- inborn
- unlearned
- unconcious
- cannot improve them
What are the types of reflexes?
Somatic Reflexes
-skeletal muscle
Visceral Reflexes
-internal smooth/cardiac muscle and glands
What is necessary for a reflex arc?
- Sensory receptor
- Sensory (afferent) neuron
- center of integration with association neuron
- motor (afferent) neuron
- effector
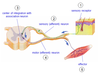
Discuss the reflex arc as a feedback system

What are the components of the stretch reflex?
Segmental - one segment of spinal cord
Monosynaptic - one synapse
Muscle spindle - a receptor that fires AP when stretched
Muscle tone
Ipsilateral - same side leg/spinal cord fires
Reciprocal innervation - inhibits the antagonist muscles

What are the components of the flexor, withdrawal, reflex?
Intersegmental - send signals to association neurons above/below which signal flexor motor units and inhibit extensor
Polysynaptic - greater than 1 synapse
Ipsilateral - same side
Pain receptor - nocireceptors commonly involved in this reflex
Role of association neurons
Reciprocal innervation - inhibits extensor muscles
-inhibitory and excitatory neurons

What are the components of the crossed extenor reflex?
Intersegmental - send signals to association neurons above/below which signal flexor motor units and inhibit extensor
Polysynaptic - greater than 1 synapse
Contralateral- both sides
Pain receptor - nocireceptors commonly involved in this reflex
Role of association neurons
Reciprocal innervation - inhibits flexor muscles
-inhibitory and excitatory neurons


