Male Reproductive System Flashcards
4 components of the male reproductive system
1) testes
2) duct systems
3) accessory glands
4) penis
4 portions of the duct system
1) ductuli efferentes
2) epididymis
3) ductus deferens
4) ejaculatory ducts.
Function of male reproductive system
1) produce spermatoza and seminal flui
2) endocrine function: testosterone produced inside the testes by laydik cells.
the ductus deferens runs from the __- to the ___.
scrotum to the urethra
Testes are surrounded by a ___ ___ ___ connective tissue capsule called ___ ___
DENSE IRREGULAR FIBROUS connective tissue known as the TUNICA ALBUGINEA.
most capsules in the body are made of what type of CT?
dense irregular fibrous ct.
the tunica albuginea gives rise to CT ___ that divide the testis into about 250 lobuels
SEPTA
function of testes
testes are paired glands with both exocrine (spermatozoa) and endocrine (testosterone) functions in laydik cells.
testes contain ___ ___ which is where sperm cells are produced.
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
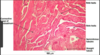
Label the image

seminiferous tubule

outline the procession of sperm from the seminiferous tubules
seminferous tubules –> straight tubules –> rete testes –> ducte efferentes –_>epididymis –> vas deferens
the _____ houses the rete testis, which an indentation in the testes where straight tubules run into
the mediastinum
label

Testes slide

each lobule of the testest made of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue contains 1-4 ___ ____. Each tubule is a loop attached by a ____ tubule to the ___ ___, a maze of channels embedded in the medianedatstinum. From the __ ___, sperm moves to the ___
each lobule of the testest made of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue contains 1-4 seminiferous tubules. Each tubule is a loo attached by a STRAIGHT tubule to the RETE TESTIS, a maze of channels embedded in the medianedatstinum. From the RETE TESTES, sperm moves to the EPIDIDYMIS
Each lobule contains 1-4 coiled ___ __, and ___ connective tissue.
seminiferous tubules, and loose connective tissue aka INTERSTITIAL CT
the seminiferous tubules are sites of ____
spermatogenesis
3 cells that make up the seminiferous tubules and function
1) sertoli cells: structural support
2) myoid cells: modified mucus cells
3) spermatogenic cells: makes germinal epithelium which develops into mature sperm cells
which type of epithelium gives rise to mature sperm cells
germinal epithelium
Capsules are made of ____, where as interstitial tissues are made of ____
capsules are often made of dense irregular fibrous connective tissues, whereas interstitial tissues are made of areolar.
____ tissue lies in between seminiferous tubules. Which types of cells and fibers are present in this tissue?
intersitial tissues are between seminiferous tubules. contain:
1) interstitial cells aka LAYDIC cells.
2) fat droplets
3) areolar connective tissue (collagenous and elastic fibers)
surrounding each seminigerous tubules are ___ cells, which contract to help move sperm out of the tubule into the straight tubule
MYOID CELLS.
are spermatogonia diploid or haploid. which types are in a seminiferous tubule?
they are DIPLOID, located near the basement membrane.
type A: on the edges.
type B; a bit less on the edges, has an OBVIOUS nucleus and nucleolus.
Primary spermatocytes undergo _____ and are located_
primary spermatocytes undergo MEOSIS and are located closer to the lumen of the tubule.
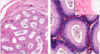
label

M- myoid cells
IC= interstitial cells
SC= sertoli cells
SG= spermatogonia
label cell types

observe seminiferous tubule cell types in lab manual

sertoli cells are joined by ___ ___ and are intimately associated with spermatogonia cells. What is the function?
joined by junctional complexes. Functions:
1) protection and nourishment of spermatogenic cells
2) phagocytosis.
spaces between seminiferous tubules are ___ connective tissue. Contains:
loose connective tissue (areolar). contains:
1) lymphatic and blood vessels
2) nerves
3) interstitial cells of leydig which produces testosterone
straight tubules are aka ___ ___
tubuli recti
T/F tubuli recti (straight tubules) contain germinal epithelium
false. but they do have sertoli support cells.
seminiferous tubules are lined with ___ epithelium, whereas rete testes are lined with ___ ___ epithelium and are located within the mediastinum of the testical
seminiferous tubules are lined with GERMINAL epithelium, whereas rete testes are lined with SIMPLE CUBOIDAL epithelium