Condition- Aortic Dissection Flashcards
What is an aortic dissection?
A condition where a tear in the aortic intima allows blood to surge into the aortic wall, causing a split between the inner and outer tunica media, creating a false lumen
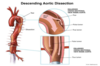
What are the two classifications of aortic dissection and which is the most common?
- Type A: ASCENDING Aorta: Most common (70%)
- Type B: DESCENDING Aorta: Less common (30%) Distal to the subclavian artery

Descirbe the pathophysiology of aortic dissection
- An intimal tear is the initial event
- Subsequent degeneration of the medial layer of the aortic wall
- Blood then passes through the media, propagating distally or proximally and creating a false lumen
- As the dissection propagates, flow through the false lumen can occlude flow through branches of the aorta
List some risk factors for developing Aortic Dissection. What is the main RF?
- HYPERTENSION-often poorly controlled
- Aortic Atherosclerosis
- Smoking
- Usually in their 50s
- Iatrogenic- angioplasty etc.
- Younger patients may have:
- Connective-tissue disorder (SLE, Marfan’s, Ehlers-Danlos)
- Recent history of heavy lifting
- cocaine use
- Congenital cardiac abnormalities
- FHx of aortic aneurysms, dissection, or a connective-tissue disorder
Describe the chest pain experienced by someone with aortic dissection
- S: Central
- O: Acute onset
- C: TEARING or RIPPING chest pain
- R: May radiate to the back in between the shoulder blades
- S: severe
Describe some of the other symptoms that may be experienced dependent on which branches of the aorta are obstructed.
* Go through the different branches and think about what could happen if they were occluded
- Carotid: Hemiparesis, dysphasia, syncope
- Coronary: Chest Pain (MI)
- Subclavian: Ataxia, loss of consciousness
- Anterior Spinal: paraplegia
- Coeliac: Abdo pain
- Renal: Anuria, renal failure
List some of the signs of Aortic Dissection on physical examination
- Distolic Murmur on the back below left scapula (crescendo pattern)
- Blood pressure differences >20mmHg between two arms
- Wide pulse pressure
- Hypertension
- Signs of aortic regurgitation:
- High volume collapsing pulse
- Early DBP over aortic area
- May be palpable abdo mass
A difference in blood pressure greater than xmmHg between the two arms is suggestive of aortic dissection?
20mmHg
Why might you get hypotension in a patient with aortic dissection. How could you check for this
Hypotension may suggest tamponade
Check for pulsus paradoxus = abnormally large decrease in systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration
Which investigations could you order for someone with suspected aortic dissection? What is the GOLD STANDARD + FIRST LINE investigation?
- CT and Echocardiography- can visualise intimal flap
- ECG- to rule ou Myocardial Ischaemia. Should be normal. If MI get ST elevation or ST depression+ T inversion
- Bloods
- FBC- anaemia
- X-match
- U&Es: renal function
- LFTs: clotting screen too
- Lactate: indicates malperfusion
- Cardiac enzymes: to rule out MI
- CXR
- Rule out pulmonary causes. May also see widened mediatinum

