8 The endocrine system Flashcards
What is homeostasis?

What is the difference between circulating & local hormones?

What is a non-biological example of Negative feedback?

Describe the role of insulin and glucagon in this particular negative feedback loop.

Give an example of a positive feedback loop in the body.
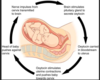
Describe the major differences between positive and negative feedback loops.
- Negative feedback loop is used more commonly than positive feedback loop.
- Negative feedback loops are involved to correct deviations of temperature, pH and many more internal variables, whereas positive feedback loops are involved to maintain specialized changes.
- Negative feedback loops involve in maintaining body temperature, pH, etc., whereas positive feedback loops involve in blood clotting and uterus contractions, in childbirth.
- Negative feedback loops always help to maintain homeostasis, whereas positive feedback usually destabilizes the systems in the body.
Hormone levels are regulated by these complex feedback loops that may be influenced by??
- Signals from the nervous system (neural stimuli)
- Chemical changes in the blood (humoral stimuli)
- Other hormones (hormonal stimuli)

Complete this sentence
Hormones affect only specific ____ ____ by (chemically) binding to specific receptors.
Hormones affect only specific target cells by (chemically) binding to specific receptors.
What are the 8 endocrine glands the IB requires you to know?
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
pineal gland
thyroid gland
adrenal glands
pancreas
ovaries and testes.
Where are these 8 endocrine glands located in the body?

Complete this table.


Which two endocrine glands are most responsible for homeostasis?
1. The hypothalamus.
It’s the link between the endocrine system and the nervous system. It also communicates directly with the pituitary gland. Even storing ADH and oxycontin in the pituitary gland.
2. The pituitary gland.
Known as the master gland. Stores ADH and oxycontin from the hypothalamus. It also receives signaling molecules from the hypothalamus, which triggers the release of other hormones.
Whats does the hormone ADH (Anti-diuretic hormone) do, and which gland releases it?
Controls the ability of water to pass through the cells in the walls of the collecting ducts. If no ADH is present, then no water can pass through the walls of the ducts. The more ADH present, the more water can pass through.
Basically ADH is crucial to maintain proper hydration, especially during exercise.
Released by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary until it sent into the body.
What does oxycontin do and which gland releases it?
Oxytocin is involved in a variety of processes, such as body temperature, sleep cycles, and the release of breast milk.
It is released by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary.
Which of these hormones are stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary?
A. GHIH and GHRH
B. Oxytocin and ADH
C. Adrenaline and testosterone
D. Prolactin and GH
B.
Oxytocin and ADH
The posterior pituitary doesn’t produce any hormones on its own, rather, it stores and secretes two hormones made in the hypothalamus (oxytocin and ADH)

