Acne Flashcards
(21 cards)
What type of bacteria is Propionibacterium acnes?
Gram-positive rod
Epidemiology Acne Vulgaris
- affects around 80-90% of teenagers
- acne may also persist beyond adolescence, with 10-15% of females and 5% of males over 25 years old being affected
Pathophysiology of acne
- follicular epidermal hyperproliferation → formation of a keratin plug →obstruction of the pilosebaceous follicle
- activity of sebaceous glands may be controlled by androgen, although levels are often normal in patients with acne
- colonisation by the anaerobic bacterium Propionibacterium acnes
- inflammation
Presentation of acne
Non-inflammatory:
- Open/black comedome
- Closed/White comedome
Inflammatory:
- Papules
- Pustules
- Nodules
- Cysts

Types of scars in acne
- ice-pick scars
- hypertrophic scars

Types of comedones on both ends of the spectrum of acne severity (2)
- mild end of spectrum→ comedomal acne, open comedomes → blackheads
- more severe end → nodulocystic acne → leaves scarring
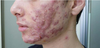
What’s acne fulminans?
Acne fulminans
- very severe acne
- associated with systemic upset (e.g. fever)
- Hospital admission is often required and the condition usually responds to oral steroids
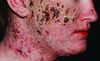
Treatment of different severites of acne
Mild
- Comedonal – topical retinoid
- Inflammatory – topical antimicrobial/antibiotic
Moderate
- comedonal – topical retinoid
- inflammatory – oral
- Tetracycline
- Macrolide
- Trimethoprim
- Spironolactone
Severe
- Oral Isotretinoin
Considerations if treating acne with Tetracycline
- Not <12 yo
- Ensure not pregnant
- Take night
- Take with food
- Not with milk
- Caution of headache
- Caution if on holiday
- Interactions
Considerations if treating acne with timethoprim
- Ensure not pregnant
- 300mg BD
- Interactions
- Bloods baseline, every 6-8 weeks (bone marrow, renal)
Name (2) oral retinoids
- Roaccutane
- Isotretinoin
SEs of oral retinoids
- Dry lips and skin
- Epistaxis
- Teratogenicity
- Depression / Suicide
- Abnormal LFTs, raised lipids
- Initial drop in Neutrophils
- Muscle pains
- Raised intracranial pressure
Can we combine oral retinoid and tetracycline?
Do not combine with tetracyclines as both raise ICP
Women in child-bearing age and prescribing oral retinoid. What to consider?
Women of a child bearing age need to be on 2 forms of contraception for 1 month before, during and 1 month after.
Can oral retinoid be prescribed if someone has a Hx of depression?
History of mental health disease – avoid isotretinoin
What’s oral retinoid class and MoA?
Derived from Vitamin A
MoA: Shrinks sebaceous unit, stabilises keratinisation and reduces inflammmation
Algorithm for acne treatment

Acne vulgaris vs acne rosacea - differences in features
Acne vulgaris:
- comedomes or nodulocystic
- commonly in teenagers
- affecting the face chest and back
Rosacea:
- no comedomes
- only papules and pustules with erythema, telangiectasia and flushing
- mainly affecting the central face
- older age group
Relate pathophysiology of acne to its treatment options
- P. acne bacteria → Abx: anti-inflammatory and antibacterial. Benzoyl Peroxide – antibacterial
- Chronic inflammation (due to bacteria) topical retinoid – anti-inflammatory and comedolytic
- Increased sebum production →Isotretionon – reduces sebum and inflammation
Features of acne rosacea
- typically affects nose, cheeks and forehead
- flushing is often the first symptom
- telangiectasia are common
- later develops into persistent erythema with papules and pustules
- rhinophyma
- ocular involvement: blepharitis
- sunlight may exacerbate symptoms/

Management of Acne Rosacea
- topical metronidazole may be used for mild symptoms (i.e. Limited number of papules and pustules, no plaques)
- topical brimonidine gel may be considered for patients with predominant flushing but limited telangiectasia
- more severe disease is treated with systemic antibiotics e.g. Oxytetracycline
- recommend daily application of a high-factor sunscreen
- camouflage creams may help conceal redness
- laser therapy may be appropriate for patients with prominent telangiectasia
- patients with a rhinophyma should be referred to dermatology


