Benign skin conditions Flashcards
(30 cards)
Features of seborrhoeic keratoses
- large variation in colour from flesh to light-brown to black
- have a ‘stuck-on’ appearance
- keratotic plugs may be seen on the surface
- very common, related to skin aging
- an occur anywhere other than palms and soles and mucous membranes
Management of seborrhoeic keratoses
- reassurance about the benign nature of the lesion is an option
- options for removal include curettage, cryosurgery and shave biopsy
Spot diagnosis
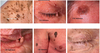
seborrhoeic keratosis
Spot diagnosis
Seborrhoeic keratosis
Spot diagnosis

Seborrhoeic keratoses
Another name for cherry hemangiomas
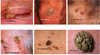
Cherry haemangiomas (Campbell de Morgan spots)
What are cherry haemangiomas?
Cherry haemangiomas (Campbell de Morgan spots)
- benign skin lesions which contain an abnormal proliferation of capillaries
- unknown cause

Features of cherry haemangiomas
aka Campell De Morgan spots
- They are more common with advancing age and affect men and women equally
- May develop on any part of the body but they appear most often around the mid trunk
- Increase in number from about the age of 40
- erythematous, papular lesions
- typically 1-3 mm in size
- non-blanching
- not found on the mucous membranes
Management of Cherry Haemangiomas
As they are benign no treatment is usually required
Spot diagnosis

Cherry haemangioma (Campbell De Morgan)
Spot diagnosis

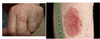
Pyogenic granuloma
What’s Pyogenic Granuloma
Pyogenic granuloma
- a relatively common benign skin lesion
- name is confusing as they are neither true granulomas nor pyogenic in nature
- multiple alternative names e.g. ‘eruptive haemangioma’
Features of pyogenic granuloma
- most common sites are head/neck, upper trunk and hands
- Lesions in the oral mucosa are common in pregnancy
- initially small red/brown spot → rapidly progress within days to weeks forming raised, red/brown lesions which are often spherical in shape
- the lesions may bleed profusely or ulcerate
Management of pyogenic granuloma
- lesions associated with pregnancy often resolve spontaneously post-partum
- other lesions usually persist
- Removal methods include curettage and cauterisation, cryotherapy, excision
Spot diagnosis

Pyogenic granuloma
What’s dermatofibroma?
- Solitary dermal nodules
- Usually affect extremities of young adults
- Lesions feel larger than they appear visually
- Histologically they consist of proliferating fibroblasts merging with sparsely cellular dermal tissues
-No treatment required if diagnosis is confident
Dermatofibroma O/E
- Site of minor trauma – insect bite
- Brownish/red dermal lesion
- Feels firm
- Pinching the tumour between fingers leads to dimpling / sinking down into the dermis
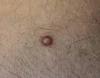
Dimple / buttonhole / pinch sign = ?
Dimple / buttonhole / pinch sign = dermatofibroma
What’s Congenital Melanocytic Naevi
- Typically appear at, or soon after, birth
- Usually greater than 1cm diameter
- Increased risk of malignant transformation (increased risk greatest for large lesions)

What’s atypical naevus syndrome?
- Atypical melanocytic naevi that may be autosomally dominantly inherited
- Some individuals are at increased risk of melanoma (usually have mutations of CDKN2A gene
- Many people with atypical naevus syndrome AND a parent sibling with melanoma will develop melanoma
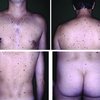
Actinic keratosis O/E
- Flaky / keratotic patches
- Bald scalps, foreheads, ears, dorsum of hands and forearms
- Feel crusty
What’s an epidermoid cyst?
- Common and affect face and trunk
- They have a central punctum, they may contain small quantities of sebum
- The cyst lining is either normal epidermis (epidermoid cyst) or outer root sheath of hair follicle (pilar cyst)
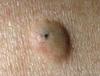
What’s actinic keratoses?
Actinic, or solar, keratoses (AK)
- a common premalignant skin lesion
- develops as a consequence of chronic sun exposure
Features of actinic keratoses
- small, crusty or scaly, lesions
- may be pink, red, brown or the same colour as the skin
- typically on sun-exposed areas e.g. temples of head
- multiple lesions may be present