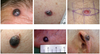
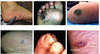
Skin cancer Flashcards
(43 cards)
Types of skin cancer
1. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
2. Melanoma
3. Premalignant Conditions
- Bowens Disease
- Actinic Keratosis
What’s the most common skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinomas are the commonest form of skin cancer making up 75% on the NMSC group
Name (2) premalignant skin cancer conditions
- Bowens Disease
- Actinic Keratosis
An 80 year old lady presents with a 2 year history of a pigmented lesion on the right cheek. Slowly increasing in size. On history alone what is the most likely diagnosis?
A: Melanoma
B: Lentigo maligna
C: Basal cell carcinoma
D: Squamous cell carcinoma
B. Lentigo maligna
A 30 year old lady presents with a 5 year history of a lesion on the right upper back. Slowly increasing in size. History of excessive use of sun beds. 9mm pink nodule with small amount of central keratin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A: Melanoma
B: Basal cell carcinoma
C: Squamous cell carcinoma
D: Seborrhoeic keratosis
B. Basal Cell Carcinoma

D: Seborrhoeic keratosis
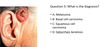
C: Squamous cell carcinoma
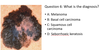
A. Melanoma
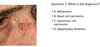
B. Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for skin cancer
- Increasing age
- Gender: M>F
- Family history (PATCH gene: tumour suppressive)
- Previous personal history of BCC
- Photodamage
- Fair skin, blue eyes, previous sunburn, sunbed use
- Immunosuppressed
- Diseases: e.g cutaneous lupus, naevus sebaceous, Gorlin syndrome
- Previous ionizing radiation, arsenic exposure
Features of Basal Cell carcinoma
- Commonly affects head and neck
- Slow growing papule, nodule
- Skin coloured, pink or pigmented
- Can bleed or ulcerate
- Very rarely metastasise
Different subtypes of Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Nodular
- Morphoeic
- Infiltrative
- Superficial
- Basosquamous
Spot diagnosis
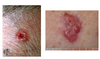
Basal Cell Ca
Spot diagnosis
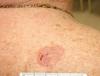
Basal Cell Carcinoma (superficial type)
Management of Basal Call Carcinoma
Surgery
- Diagnostic biopsy initially
- Excision
- Moh’s micrographic surgery
Radiotherapy
Management of superficial variant of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Superficial variant:
- Cryotherapy
- Curettage and cautery
- Topical treatment
- 5-FU; Imiquimod; Ingenol mebutate
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
Another name for Gorlin Syndrome
Basal cell naevus syndrome
Features of Gorlin syndrome
Features:
- Multiple BCC’s
- Young age
- Calcified falx cerebri
- Broad forehead
- Odontogenic cysts jaw
- Abnormal ribs (bifid, fused, missing)
- Palmar/plantar pitting
- Other tumours – melanoma, breast carcinoma, NHL, ovarian fibroma

Management of Gorlin Syndrome
- Excision
- Vismodegib → binds to and inhibits the transmembrane protein Smoothened homologue (SMO) to inhibit the Hedgehog signalling pathway
Pathogenesis of Gorlin syndrome
PATCH gene Chr 9; SUFU gene Chr 10
(defective tumour suppressor genes)
Simple pathophysiology of Squamous cell carcinoma
Cancer arising from keratinocytes in the epidermis
Risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma
- excessive exposure to sunlight / psoralen UVA therapy
- actinic keratoses and Bowen’s disease
- immunosuppression e.g. following renal transplant, HIV
- smoking
- long-standing leg ulcers (Marjolin’s ulcer)
- genetic conditions e.g. xeroderma pigmentosum, oculocutaneous albinism
Features of squamous cell carcinoma
- Short history – weeks to months
- Rapidly enlarging papule/nodule
- Tender
- Can ulcerate
- Commonly on sun-exposed sites
Spot diagnosis
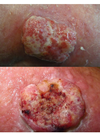
Squamous cell Ca