Acute Abdomen Flashcards
(144 cards)
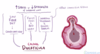
What type of pain would someone with appendicitis complain of?
central abdominal pain that moves into the right iliac fossa
Typically, how does someone with appendicitis present?
- tends to be a young person (5 - 40 years old)
- acute onset within 12 - 24 hours
- present with umbilical pain that moves to the right iliac fossa
- nausea and/or vomiting
- diarrhoea or constipation
- fever
What might be present on general inspection and palpation of someone with appendicitis?
- in the early stages there is general pain and peri-umbilical pain on palpation
- in the later stages, the person will often stay very still due to peritonitis
- this occurs after the appendix has ruptured, and the peritoneum has become inflamed
on palpation, there will be right iliac fossa pain

What signs might be present in appendicitis?
- Rovsing’s sign
- Cope’s sign
- Psoas sign
- rebound tenderness
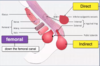
What is Rovsing’s sign?
- pain is greater in the RIF than the LIF when the LIF is pressed
- this is specific to appendicitis

What is Cope’s sign?
- there is pain on passive flexion and internal rotation of the hip
- it indicates irritation to the obturator internus muscle
- the appendix becomes inflamed and enlarged and may come into contact with the obturator internus muscle when this move is performed

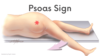
What is Psoas sign?
- there is pain on extending the hip
- pain indicates an inflamed appendix overlying the iliopsoas muscles
- this only occurs with retrocaecal appendix
- (as the iliopsoas muscle is retroperioneal)
- this indicates that the inflamed appendix sits behind the caecum
When might rebound tenderness be evident in appendicitis?
What is this?
- this indicates that the infection is involving the peritoneum
- there is pain upon removal of pressure from the abdomen rather than application of pressure to the abdomen
- this is indicative of peritonitis
- there may also be abdominal guarding - the abdominal muscles tense up to avoid pain
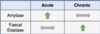
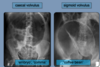
What are the investigations involved in appendicitis?
- first line investigation is CT abdomen
- USS can be done if CT is not available
- this will show increased appendix diameter and increased wall enhancement
- bloods - which will show leucocytosis and elevated CRP

What is the most common cause of appendicitis in adults?
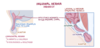
- appendicitis results from obstruction of the appendix lumen
- this may be due to a fecalith (hardened lump of faecal matter) that wedges itself within the lumen
- it can also be due to undigested seeds or pinworm infections

What is a common cause of appendicitis in adolescents?
lymphoid hyperplasia
- this involves growth of the lymphoid follicles, which are dense collections of lymphocytes
- these reach their maximum size in adolescence and can obstruct the lumen of the appendix
- when exposed to viral infections or immunisations, the follicles can increase in size
How does obstruction of the lumen of the appendix lead to pain?
- the intestinal mucosa secretes mucus and fluids to keep pathogens from entering the bloodstream and to keep the tissue moist
- even when obstructed, the appendix keeps secreting
- there is a build up of fluid and mucus in the appendix, which increases the pressure
- the appendix gets bigger and physically pushes on afferent visceral nerve fibres nearby, causing pain
Why is there is an increase in serum WBC count in acute appendicitis?
What processes have to occur prior to this for it to occur?
- as there is an obstruction, flora and bacteria in the gut are trapped
- E. coli and bacteroides fragilis
- these bacteria are now free to multiply
- this causes the immune system to produce WBCs, which leads to the build up of pus in the appendix
What happens if the obstruction in the appendix persists past the build-up of pus in the appendix?
- the pressure in the appendix increases even further
- it expands and begins to compress small blood vessels that supply it with blood and oxygen
- without oxygen, the cells in the wall of the appendix become ischaemic and die
- these cells were responsible for secreting mucus and keeping bacteria out, so now the growing colony of bacteria can invade the wall of the appendix

What leads to rupture of the appendix?
What happens if the appendix ruptures?
- as more cells in the wall of the appendix die, it becomes weaker and weaker
- in a small proportion of patients, the appendix wall becomes so weak that it ruptures
- this leads to bacteria entering into the peritoneum and causing peritonitis
- this leads to abdominal guarding and rebound tenderness at McBurney’s point
What is the most common complication of a ruptured appendix?
- formation of a periappendiceal abscess
- this is a collection of fluid and pus around the ruptured appendix
- sometimes smaller subphrenic abscesses can form
- these are below the diaphragm, but above the liver/spleen
What is the treatment for appendicitis?
appendicetomy
- this is surgical removal of the appendix, followed by antibiotics
- if there is an abscess, this must be drained first

What scoring system is used to determine the severity of appendicitis?
Alvarado score
- score of 1 to 4 is discharged
- score of 5 to 6 is observed
- score of 7 to 10 needs surgery

Which antibiotics are given following appendicetomy?
- cefotaxime
-
metronidazole
- this is an anti-anaerobe antibiotic for the gut
What are the 3 possible complications of appendicitis?
- perforation
- appendix abscess
-
appendix mass
- the inflamed appendix becomes covered in omentum and forms a mass
- this tends to occur in older men who avoid coming to the doctors when they get pain


B-hCG test
- the first line investigation in any woman with an abdominal pathology should ALWAYS be a pregnancy test
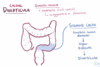
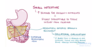
What is meant by diverticulosis?
- the presence of diverticulae
- these are outpouchings of the colonic mucosa and submucosa throughout the large bowel
-
high pressure in the bowel causes these outpouchings to form
- e.g. chronic constipation

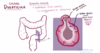
What is meant by diverticulitis?
Which part of the bowel is more commonly affected?
- acute inflammation and infection of the diverticulae
- most commonly affects the sigmoid colon