Acute Eye Flashcards
(95 cards)
What investigation is useful to determine areas of epithelial loss?
Fluorescein (blue light)
Blood in the anterior chamber of the eye is called
Hyphaema
Commotio retinae is AKA…
Bruised retina
What test is useful to see if there is a penetrating injury in the eye?
Fluorescein (blue light)
Where do small particles commonly lodge in the eye?
Sub-tarsal, conjunctiva, corneal (most common)
Intra-ocular foreign bodies are most commonly associated with what activity/ injury mechanism?
Fast moving objects (e.g. hammer and chisel injuries).
What investigation should always be performed in suspected foreign body of the eye?
X-ray (for intra-ocular foreign bodies)
Alkali burn injures to the eye will penetrate little/lots?
Lots (penetrates deep to the intra-ocular structures)
Acid burn injuries penetrate little/lots?
Little (these will coagulate the eye proteins)
Ciatrising changes to the conjunctiva and cornea suggests what type of injury?
Alkali burn
Limbal ischaemia is a poor prognostic factor for what injury type?
Alkali burns
How should eye chemical burns be managed? (5)
1) Quick history 2) Check Toxbase if available 3) Check pH of eye 4) Irrigate +++ (at least 2L of saline) 5) After this check slit-lamp
List some causes of acute vision loss
Vascular changes, vitreous haemorrhage, retinal detachment, wet-type ARMD, closed angle glaucoma
Is CRAO painful?
No, it is a cause of sudden painless visual loss
CRAO causes what degree of vision loss?
Profound
A CRAO will have what fundus appearence
Pale, oedamteous, small retinal vessels
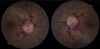
What does this fundoscopy show?
CRAO (pale, cherry red spot)
How is CRAO managed? (<24 hours presentation)
Ocular massage (try to convert CRAO to BRAO)
Transient CRAO leads to what visual change? How is it treated?
Amaurosis fugax (usually lasts 5 minutes).
Treated with urgent stroke clinic referal and aspirin.
What are some signs of CRVO? (3)
Retinal haemorrhage, dilated tortuous veins, disc swelling and macular swelling
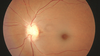
What does this fundoscopy show?

CRVO (haemorrhages, dilated veins and disc swelling)
How is CRVO treated?
Anti-VEGF intravitreal
Older treatment laser treatment to avoid haemorrhages
Treat risk factors (HT, DM)
What does this fundoscopy show?

BRVO