Microbiology Flashcards
(64 cards)
What is the Gram appearance of Neisseria species?
Gram negative cocci
What is the Gram appearance of Pseudomonas species?
Gram negative bacilli
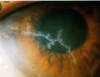
Keratitis is
Inflammation of the cornea
Endopthalmitis is inflammation of the
Entire globe
Commonest 3 causes of neonatal conjunctivitis?
1) S. aureus 2) N. gonorrhoea 3) C. trachomatis Refer ALL neonatal conjunctivitis to ophthalmology
Commonest 3 causes of bacterial conjunctivitis (non-neonate)?
1) S. aureus 2) S. pneumoniae 3) H. influenzae
Where should a swab for bacterial conjunctivitis be taken?
Fornix (using analgesic drops)
What’s the standard treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis?
Chloramphenicol drops QDS
Chloramphenicol must be avoided in which history
Aplastic anaemia or allergy
Commonest 3 causes of viral conjunctivitis
Adenovirus Herpes zoster Herpes simplex
What illness tends to precede a viral conjunctivitis?
Upper RTI
What’s the main symptom/sign difference between bacterial & viral conjunctivitis?
Viral tends to be a more watery discharge. Bacterial tends to be mucus discharge.
What should raise suspicion of chlamydia conjunctivitis? (3)
Chronic eye infection, unresponsive to treatment, bilateral infection (if young adults).
Why is it important to define and diagnose cases of chlamydia?
Needs contact tracing
“Rice-grain follicles” is pathognomonic of which infection?
Chlamydia conjunctivitis
Why is chlamydia serious in eye infections?
Can cause irreversible scarring
A collection of white cells in the anterior eye is termed what?
Hypopyon
What is the treatment for bacterial keratitis like? (3)
1) Hourly eye drops (Day and night) 2) Scalpel to remove tissue for microbiology C&S 3) Daily review
Dendritic ulcer in the eye is characteristic of which type of infection?
Viral (especially herpes)
T/F: Herpetic keratitis is usually painless.
False - very painful
Which medication class is absolutely contraindicated in herpetic keratitis? Why is this particular medication sometimes still used?
Steroids (can cause a corneal melt and perforated cornea). Clinicians sometimes confuse herpetic keratitis with uveitis (inflamamtion) and prescribe steroids.
How is herpetic keratitis treated?
Zyvrax.
A geographical ulcer is indicative of what
A patient who was given steroids to treat their herpetic keratitis (causing an ulcer/ perforation of eyeball)
Which viral infection causes darkening of the cornea?
Adenoviral keratitis