Anatomy Flashcards
(104 cards)
What are the bones of the orbit? (7)
Frontal, Zygomatic, Maxilla, Nasal, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Lacrimal
Label the structures (bones and any landmarks seen)

A: Maxilla (infraorbital foramen)
B: Ethmoid
C: Frontal (supraorbital notch on right)
D: Sphenoid (optic canal)
E: Sphenoid (superior orbital fissure)
F: Lacrimal
G: Nasal
In orbital blowout fracture, which bone tends to be ruptured?
Zygoma
Which muscle is this? What are the parts (A and B)?
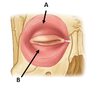
Orbicularis oculi (CN VII)
A: Orbital part
B: Palpebral part
List the parts of the orbital fascia

A: Levator palpebrae superoris tendon
B: Superior tarsus
C: Medial palpebral ligament
D: Inferior tarsus
E: Orbital septum
F: Lateral palpebral ligament
What kind of substance do the tarsal glands secrete?
Lipid
Label the surface anatomy of the eye

A: Iris
B: Conjunctival blood vessel
C: Lacrimal lake
D: Inferior lacrimal papilla & punctum
E: Lower eyelid lined by palpebral conjunctiva (central part = bulbous conjunctiva)
F: Conjunctival fornix
G: Sclera
H: Limbus (corneo-scleral junction)
I: Location of the lacrimal gland
Which innervation produces lacrimal fluid?
CN VII parasympathetic
Where do the tears drain in the eye? Where do they drain to in the nose?
Drain to lacrimal puncta, eventually reach inferior meatus in the nasal cavity (through the nasolacrimal duct)
What are the 3 layers of the eye?
Fibrous (outer layer containing sclera and cornea)
Uvea (vascular middle layer containing the iris, ciliary body and choroid)
Retina (inner photosensitive layer containing the photoreceptors)
The ciliary body is located in which layer of the eye?
Uvea/ vascular layer
What are the 2 parts of the eye? List any sub-parts?
Anterior and posterior segment.
Anterior segment is in front of lens. Divided into anterior (between cornea and iris) and posterior (between iris and suspensory ligaments) chambers.
The posterior segment is everything behind the lens
Which humours are present in each part of the eye?
Anterior segment = aqueous
Posterior segment = vitreous
Where is 2/3rds of the refractive power of the eye held?
Cornea
Floaters are located within which part of the eye??
Posterior segment (within the vitreous humour)
What is the iridocorneal angle?
Angle between the iris and cornea
Describe the circulation of aqueous humour (4)
1) Produced in the ciliary body
2) Circulates within the posterior chamber to nourish the lens
3) Passes through pupil into anterior chamber and nourishes cornea
4) Is reabsorbed into the scleral venous sinus (at the Canal of Schlemm located at the iridicorneal angle)
The opthalmic artery is a branch of which artery?
Internal carotid
List the parts of the dural venous sinus

A: Internal carotid artery
B: Cavernous sinus
C: Ophthalmic artery (coming off the internal carotid)
D: Pituitary
E: CN II (optic)
F: CN III (oculomotor)
G: CN IV (trochlear)
H: CN V1 (opthalmic division)
I: CN V2 (maxillary division)
J: CN VI (Abduscens)
K: Sphenoidal Sinus
The opthalmic artery enters the eye within CN II, true or false?
False - it’s the central artery of the retina (which is a branch of the ophthalmic artery)
T/F: The retina has 2 veins draining it.
False - only 1 (central vein of the retina).
Which structures drain the orbit? (venous)
Superior and inferior ophthalmic vein
Where do the opthalmic veins drain to?
Cavernous sinus (through the superior orbital fissure)
Where does CN II present in the fundus of the eyeball?
Optic disc (blind spot)