Afib and Hyponatremia Flashcards
(36 cards)
Hyponatremia diagnostic approach
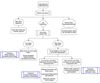
Hyponatremia workup and management

Management and symptom control of Afib
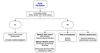
When controlling heart rate for Afib. . .
. . . 110 is a decent target – you don’t need to fully normalize HR, you probably won’t be able to
Risk calculators in Afib management
CHADS-VASc (for stroke risk)
HAS-BLED (for major bleed risk)
In which patients are direct oral anticoagulants contraindicated?
Patients with some form of hemophilic disorder
Patients with prosthetic heart valves
Obese patients
In order to perform an elective cardioversion for someone, they need to be . . .
. . . anticoagulated for at least 3 weeks, OR have evidence showing there is no intracardiac clotting.
When deciding what treatment to use for atrial fibrillation, it is important to take into account whether or not the patient is in, . .
. . . congestive heart failure
Rate control agents like metoprolol or diltiazem may make CHF worse at high doses. Rhythm agents may be a better choice in these cases, however we don’t like to keep patients on them long-term if avoidable because of side effects.
Major side effects of amiodarone
Amiodarone can cause end-organ damage to multiple organs, but most importantly:
Lung
Liver
Thyroid
Nociceptive pain circuit

Neuropathic pain circuit

Drugs for nociceptive pain don’t work for. . .
. . . neuropathic pain
WHO Pain STEP diagram (nociceptive)

Ketoralac
Particularly strong NSAID for nociceptive pain.
Only available IV. Great for acute moderate pain, but due to effects on kidneys only safe for 3-5 days.
Adverse effects and contraindications of NSAIDs

Neuropathic pain step diagram

Only approved COX-2 selective inhibitor
Celecoxib aka celebrex
Contraindicated in patients with cardiac conditions.
Opioid receptors

Opioid analgesic mechanism of action

“Morphine equivalency”
Potency of opioids and other analgesics relative to morphine
Used to compare pain medications when switching for one reason or another.
Daily limit of tylenol
4000 mg
Anesthetic vs analgesic
Analgesics selectively deactivate pain pathways
Anasthetics deactivate all sensory and motor pathways (they usually target basic nerve depolarization pathways, like Na channels, think lidocaine)
Indications for pharmacoligically treatment of delirium
Patient is a threat to self or others
Patient is removing IVs or other medical equipment necessary to their treatment and immediate health or causing traumatic injury in the process
Delirium treatment algorithm