Transitions Derm Flashcards
(114 cards)
Autosomal dominant eczema
Filaggrin mutation
Inverse psoriasis
- Likes intertrigonous areas
- No scale – very erythematous
-
In males, perineal inverse psoriasis will involve the scrotum
-
Important because tinea cruris never involves the scrotum
*
-
Important because tinea cruris never involves the scrotum
Medication-induced psoriasis
- Beta blockers
- Antimalarials (hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine)
- Lithium
- Interferons
First-line for new-onset psoriasis
Still topical corticosteroids
BUT, we don’t want to keep patients on these forever. If the psoriasis persists, we should try some non-steroid alternatives
Non-steroidal psoriasis treatments
-
Calcipotrene (Vit D analog) or Calcitirol topical cream
- Induces terminal differentiation of keratinocytes
- Risk of hypercalcemia if too much is used, for obv. reasons
-
Tazarotene topical cream
- A newer generation Vit A analog
- Targets retinoid receptor
- Contraindicated in pregnancy, for obv. reasons
-
Topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus, pimecrolimus)
- Specifically for inverse psoriasis or facial psoriasis
When psoriasis plaques are too widely dispersed, it’s time for. . .
. . . phototherapy (narrow band UVB 3x/week for 3 months, UVA for thick plaques), low-dose methotrexate, acitretin, or cyclosporine.
Arthritis mutilans
End-stage psoriatic arthritis
Indication for systemic therapy: low-dose methotrexate, cyclosporine

Cyclosporine is not a ___ option.
Cyclosporine is not a long-term option. It is a temporizing measure
Recall that it is a calcineurin inhibitor, effectively inhibiting transcription of IL-2.
Long term consequences: Immunocompromise, hypertension, adverse effects on lipid profile, nephrotoxicity
Acitretin
Oral retinoid
Used for systemic treatment of psoriasis
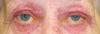
Seborrheic dermatitis at a glance
Greasy, dry, red skin with a dandrufy scale
Often perioral, around the eyes, on the nose, in the ears, or bordering the hair
Possibly due to hypersensitivity against Malassezia furfur (this is why we treat w/ ketoconazole creams)
Shared histologic hallmarks of all forms of eczema
- Spongiosis
- Epidermal changes of scale
- Parakeratosis
90% of patients who are going to have atopic dermatitis have it by age ___.
90% of patients who are going to have atopic dermatitis have it by age 5
Assocaited findings with atopic dermatitis
- Hyperlinear palms and soles (lots of crease lines)
- Keratosis pilaris (perifollicular thickening and redness)
- Ichthyosis vulgaris (diamond-shaped, fish-like scales over skin on arms/legs, especially calves, also assc. w/ filaggrin mutation)
- White dermographism (white urticarial response to koebnerizing stimulus)
Lichen simplex chronicus
Skin change due to chronic itching/scratching

Why should patients with eczema not get the smallpox vaccine?
It may get disseminated over their plaques, which have decreased immune defense capabilities
This is the same reason plaque areas are susceptible to eczema herpeticum.
Grades of steroid creams
I to VI depending on strength, with group VI being most potent.
You should know:
- Group I: Betamethasone
- Group II: Desoximetasone
- Group VI: Dexamethasone or Hydrocortisone
Absorption into skin from ointment, lotion, and cream
In terms of potency/absorption:
Ointment > Cream > Lotion
That is becase ointment is the most oil based, lotion is the most water based, and cream is in-between. You absorb better topically from more oil-based media.
Purine synthesis blockers
Azathioprine
Mycophenolate mofetil
Can be used as oral medications for topical treatment resistant eczema
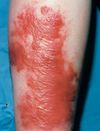
Patient with chronic lower extremity edema develops bronze coloration and skin cobblestoning of the lower extremity overlying edema. What is the likely diagnosis?
Stasis dermatitis
Unifying symptomatology of all forms of eczema
Xerotosis and pruritis
Contact dermatitis: Irritant vs allergic
- Irritant: Caustic exposure causing xerotic, pruritic rash
- Allergic: Immune-mediated process requiring previous asymptomatic exposure produces xerotic, pruritic rash – Type IV hypersensitivity (like poison ivy). Rash develops 3-4 days after secondary exposure.
Facial dermatitis is often . . .
. . . iatrogenic. Patients may be using face creams that they don’t know are acidic and leaving them on for too long, resulting in effective acid burns.
3 most common allergic dermatitis allergens
- Nickel sulfate
- Neomycin
- Balsam of Peru
Folliculitis
Infected hair follicles
Most commonly Staph. aureus
Advise to avoid touching. Treat w/ antibacterial topicals (often clindamycin) or soaps (benzylperoxide), if extensive w/ oral antibiotics