Anterior abdominal wall and peritoneum Flashcards
(55 cards)




From superficial to deep, what structures are in the:
- Upper right abdominal quadrant
- Upper left abdominal quadrant
- Lower right abdominal quadrant
- Lower left abdominal quadrant
- S: liver, body/antrum of stomach, half of transverse colon, some of small intestine; D: Gallbladder, duodenum, part of pancreas
- S: Fundus and body of stomach, half transverse colon, part of small intestine; D: pancreas, spleen
- S: Small intestine; D: Ascending colon
- S: small intestine; D: descending colon
Which quadrant would you palate if concerned about appendicitis?
Lower right
Where are the kidneys located with respect to costal margin and upper quadrants?

The abdominal aorta bifurfaces at level of […]
Umbilicus




For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation


For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation


For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation


For each structure:
- Name
- Action
- Innervation






Where is the arcuate line?
Halfway between umbilicus and pubic bone




For each structure:
- What is the name
- What is it a branch of
- Where does it travel in abdomen


What vessel assists in providing blood to the anterior abdominal if a patient has had a CABG (coronary artery bypass graft) surgery?
Inferior epigastric




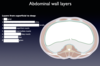
Inferior to the arcuate line, the anterior rectus sheath is made up which tissue layers?
EO aponeurosis + IO aponeurosis + transversus abdominis aponeurosis
Inferior to the arcuate line, the posterior rectus abdomins sheath is […]
Non existant - only the transversalis fascia is posterior to the RA inferior to arcuate line