Basics of Fracture Management Flashcards
(38 cards)
how is a fracture classified?
VARYING DEGREES OF STABILITY TO A TELESCOPING FORCE (longitudinal force) APPLIED AFTER REDUCTION (normal alignment) (is it stable?)
what does treatment of a fracture depend on?
Stability of fracture
Patient Factors (fitness, other injuries etc.)
Closed vs Open
Types of Fracture and Stability to shortening:
what types of stability do different kinds of fractures cause?
COMPLETE STABILITY - transverse
NO STABILITY TO SHORTENING:
- oblique
- spiral
- Comminuted
POTENTIAL STABILITY:
- oblique fractures
- < 45 degrees
As you apply a longitudinal force down in a fracture that isn’t transverse then you would find the proximal and distal segments would slide past each other

what is an open fracture?
There is a direct communication between the external environment and the fracture
usually through a break in the skin, but not always, e.g. fragments of bone from a fractured pelvis penetrating the rectum
a graze on the skin that does not penetrate the dermis over a fracture does NOT make it an open fracture
open fractures differ form closed fractures in what 2 main ways?
Higher risk of infection
Higher energy of injury
how are open fractures graded?
Gustilo grading:
Type I - low energy, wound <1cm
Type II - moderate soft tissue damage, wound 1-10cm
Type III - high energy, wound >10cm; any gunshot, farm accident:
- IIIA - soft tissue damage +++ but not grossly contaminated
- IIIB - periosteal stripping (soft tissue over bone been stripped off)
- IIIC - assoc. neurovascular complication
what is the management of open fractures?
tetanus and antibiotic prophylaxis (slows bacterial growth)
Photograph (don’t have to keep uncovering it), cover and stabilise limb (splintage)
surgical emergency:
- Some operation within 6h
- All operation within 24 hrs
early and thorough wound excision and toilet - By senior experienced surgeons (Take out everything that is dead)
do not close wound – leave skin open
repeat wound review and toilet
early definitive skin cover (5-7 days)
stabilise # definitively
? bone grafting
fasciotomies
treatment of a fracutre - what is initially done?
Immobilisation (best thing to do)
Pain relief
treatment of a fracutre - what assessment is carried out?
Clinical:
- Fracture
- Circulation (distal to fracture)
- Neurological (distal to fracture)
- Open vs Closed
Radiological
treamtent of a fracture - what definitive treatment is done?
No reduction required
Reduction required (if there is displacement - Reduce bone back to its anatomical position) - LA,GA,other
Maintenance of position:
- Conservative
- Operative
whata re the 2 types of fracture treamtent?
Conservative and operative
what is the conservative treatment of a fracture?
No Immobilisation:
- Strapping
- Brace
Immobilisation:
- Cast
- Functional Bracing
- Traction
what is the operative treatment of a fracture?
Pins
External fixators
Intramedullary rods
Screws and Plates
Conservative Fracture Treatment:
if there is No Initial Immobilisation or reduction required, then what may be done?
No support
Support:
- Strapping
- Elastic Bandage
- Brace
Conservative Fracture Treatment:
if there is Initial Immobilisation +/- Reduction, what may be done?
Cast
Functional Brace
Traction (In the medical field, traction refers to the practice of slowly and gently pulling on a fractured or dislocated body part. It’s often done using ropes, pulleys, and weights. These tools help apply force to the tissues surrounding the damaged area)

what are the cast principles?
THREE POINT LOADING
HYDRAULICS
ROTATIONAL CONTROL - By including joint above and below
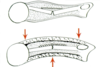
what is soft tissue hinge?
Always present
Dependent on magnitude of injury
Periosteum, interosseous membrane, septum
Muscles

what do hydraulics do?
Soft tissue can burst out with out constraint

what is functional bracing?
For long bones - Femur, tibia, humerus
Joints left free - To mobilise
Once bone “Sticky” - No longer shorten
Stops bending
Stops angulation
Allows joints to move

what is the process of traction?
AXIAL FORCE
SOFT TISSUE SLEEVE
ALIGNMENT RESTORATION
CLOSED REDUCTION
INDIRECT REDUCTION
MAINTENANCE REDUCTION
Pulls along line of limb and aligns bone

how is skin traciton done?
Applied via adhesive or non adhesive tape
CHILDREN - Gallows <12kg (child weight)
ADULT < 6LB
BLISTERING / SLOUGHING
COMPARTMENT SYNDROME
how is skeletal traction done?
Traction via bone (pin or wire)
Allows greater force/weight
Common sites:
- Femur
- Tibia
what are the different types of operative treatment?
External Fixation
Internal Fixation:
- Intramedullary Nailing
- Screw
- Plate
what are external fixators?
Fixation from outside
Pins or wires passed through skin and bone
Fixed to an external frame











