Cardiogenesis/Vasculogenesis Flashcards
Development of the Heart and major vessels (33 cards)
What marks the beginning of Vasculogenesis in the developing embryo?
What (2) types of cells primarily arise?
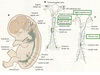
Blood islands (mesoderm aggregations) form in the Yolk Sac (additional sites of blood cells/vessels form in the placenta, umbilical cord, and embryo proper).
Blood islands segregate into Hemoblasts (future blood cells) and Endothelial cells (Forms the lining of the blood vessels).
What are the (4) Major primarily blood vessels that arise?
From where do they arise?
(2) Endocardial tubes (L&R) and (2) Dorsal Aorta (L&R); All extending the full length of the embryo.
Endocardial tubes are derived from Splanchnopleuric mesoderm, while the Dorsal Aortae are from Dorsal Mesenchyme near the Notochord
Where do the (4) major primary blood vessels converge; what is the name of this region; and what is it’s significance?
They converge at the Cardiogenic Region (horseshoe-shaped), located cranial to the Neural plate and buccopharyngeal membrane. This region will give rise to most of the tissues of the Heart.
How does lateral folding effect the Endocardial tube location? What does this facilitate?
Endocardial tubes move from Lateral to the Endoderm to a position Ventral to the Gut tube
This facilitates the fusion of the endocardial tubes to form endothelial lining (part of the Tunica Intima) of the developing Heart.

What affect does Cranial folding have on the Cardiogenic region?
During cranial folding, the fusing endocardial tubes are pulled (ventrally, caudally, then dorsally) into the thorax, dragging along the anterior portions of the Dorsal Aortae.
-Results in a single heart tube in the thoracic region
Following Cranial folding, What are the (3) major types of veins and where do they converge?
- L&R Common Cardinal Veins
- Villetine Vein
- Umbilical Vein
All veins converge at the Sinus Venosus, located at the caudal end of the developing heart tube
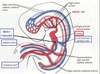
What is the Aortic sac?
The Aortic Sac is a single tube at the cranial end of the fused endocardial tubes (heart tube) which gives rise to the First Aortic Arches (L&R), continuing on as the L&R Dorsal Aortae
How many aortic arches arise and how are they oriented?
There are (5) aortic arches (numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, & 6) which travel laterally and dorsally around the developing Gut tube forming a cage-like structure.
What does the 1st arch become?
What does the 2nd arch become?
- Both the L&R 1st arch become Maxillary arteries within the Jaw
- Both the L&R 2nd arch become Stapedial arteries within the ear, however these arteries are only present during development of the ear and are not present at birth/adult

What do the 3rd arches develop into?
Both the L&R 3rd arches develop into the L&R Common Carotid
- The Internal and External Carotids sprout from the Common Carotids
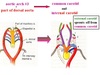
How do the 4th arches develop?
Left 4th Arch: Becomes part of the Aortic arch
Right 4th Arch: Becomes part of the Subclavian artery

How do the 6th arches develop?
Left 6th Arch: Becomes the Ductus Arteriosus; The pulmonary artery sprouts from the 6th arch
Right 6th Arch: Lost/ Disappears

Maxillary Arteries are derived from what arches?
L&R 1st Arch
Stapedial arteries are derived from which arches?
L&R 2nd Arches
The Common Carotids are derived from which arches?
L/R 3rd arches
The internal Carotid is derived from which vessels?
L&R 3rd arch + segment of the Dorsal Aorta
The External Common Carotids are derived from which vessels?
L&R Common Carotid
The Right Subclavian Artery is derived from which vessels?
Right 4th arch
Right 7th Intersegmental
Right Dorsal Aorta
The Left Subclavian Artery is derived from which vessels?
Left 7th Intersegmental
The Brachiocephalic artery is derived from which vessels?
Portion of the Aortic Sac
The Aortic Arch is derived from which vessels?
Left 4th arch
Left Dorsal Aorta segment
portion of the Aortic Sac
The Ascending aorta is derived from what vessels?
Portion of the Aortic Sac
The Descending Aorta is derived from which vessels?
Left Dorsal Aorta Segment
The Ductus Arteriosus is derived from which vessels?
Left 6th Arch