Chapter 1 - PPT Flashcards
(26 cards)
Cell Basic Anatomy Picture

Characteristicks of Living Systesm
- Metabolism
- Reproduction
- Differentiation
- Communication
- Movement
- Evolution
Transcription
DNA Produces RNA
Translation
RNA Makes Protein
Microbial Communites
Microorganisms exist in nature in populations of interacting assmeblages
Habitat (microobial)
The environment in which a microbial population lives.
Ecosystem
Refers to all living organisms plus physical and chemical constiutents of their environment.
What earthly environment is sterile?
Only molten lava.
LUCA
Last universal common ancestor
How old is the earth?
4.6 Billion Years Old
When did the first cells appear?
3.8-3.9 Billion Years Ago
When did the atmosphere stop being anoxic?
~2 billion Years Ago
When did life stop being exclusively microbial?
~1 billion years ago
Where are most microbial cells found?
Oceanic and Terrestrial Subsurfaces
The subsurface biosphere is the largest untapped biosphere on the planet.
Microbes beneath the earths surface make up as much as half of all living material on our planet
What are some positive impacts on nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
- Nitrogen fixing
- Cellulose degrading microbes in the rumen
- regenerations of nutrients in soil and water
Negative impacts of microorganisms on agriculture.
Plant and animal diseases.
What are some positive impacts of microorganisms on food?
Fermentation
What is biomediation?
The role of microbes in cleaning up pollutants.
Example: microorganisms can be used to consume spilled oils.
Lois Pasteur (1822-1895)
Discovered that living organisms discriminate between optical isomers.
Discovered alcoholic fermentations was a biologically mediated process.
Developed the germ theory that proposed and showed germs caused disease
Developed vaccines for anthrax, fowl cholera, rabies
Disproved theory of spontaneous generation: Led to the development of methods of aseptic technique)
Swan Neck Flask Experiment (Part 2)
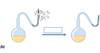
Swan Neck flask experiment part 1

Swan Neck Flask Experiemtn Part 3

Robert Koch
Demonstrated the link between microbes and infectious diseases
Developed techniques (solid media) for obtaining pure cultures of microbes
Koch’s Postulates (blue boxes)

- the suspected pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease and absent from healthy animals
- The suspected pathogen must be grown in pure culture
- The cells from a pure culture of the suspected pathogen must cause disease in a healthy animal
- the suspected pathogen must be reisolated and shown to be the same as the original



