Chapter 4 - PPT Flashcards
(61 cards)
Metabolism
–The sum total of all chemical reactions that occur in a cell
Catabolic Reactions
Energy-releasing metabolic reactions
Anabolic Reactions
–Energy-requiring metabolic reactions
Nutrients
Supply of monomers (or precursors of) required by cells for growth
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts
Essential Elements by Dry Weight in Cell

Macromolecular Composition of a Cell

Growth Factors
Organic compounds required in small amounts by certain organisms
Examples: vitamins, amino acids, purines, pyrimidines
Vitamins
Most commonly required growth factors
Most function as coenyzmes
Culture media
Nutrient solutions used to grow microbes in the laboratory
Defined media:
precise chemical composition is known
Complex media:
composed of digests of chemically undefined substances (e.g., yeast and meat extracts)
Selective Media
Contains compounds that selectively inhibit growth of some microbes but not others
IF it grows or not
Differential Media
Contains an indicator, usually a dye, that detects particular chemical reactions occurring during growth
HOW it grows in comparison
Pure culture:
culture containing only a single kind of microbe
Free energy (G):
energy released that is available to do work
Exergonic reactions
Negative deltaG0′
Release free energy
Endergonic reactions
Positive DeltaG0′
Require energy
Activation energy:
energy required to bring all molecules in a chemical reaction into the reactive state
A catalysis is usually required to breach activation energy barrier
Activation energy with and without catalyst

Red no enzyme
Green with enzyme

Catalyst:
substance that
Lowers the activation energy of a reaction
Increases reaction rate
Does not affect energetics or equilibrium of a reaction
Are not consumed or transformed by reaction


Enzymes
Biological catalysts
Typically proteins (some RNAs)
Highly specific
Function of 3D structure
Typically rely on weak bonds
Examples: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions
Active site: region of enzyme that binds substrate
Increase the rate of chemical reactions by 108 to 1020 times the spontaneous rate
Enzyme catalysis: E + S E S E + P
Catalysis dependent on
Substrate binding
Position of substrate relative to catalytically active amino acids in active site
E+SE-SE+P

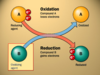
Oxidation:
the removal of electron(s)