chapter 11 Flashcards
(67 cards)
what is an intermolecular force?
attractive force that hold particles together in the condensed phases
what is a dipole-dipole interaction?
attractive force that acts between polar molecules
what is hydrogen bonding?
occurs in molecules that contain H bonded to a small, highly electronegative atoms, such as N, O, or F
what are dispersion forces?
forces that occur as a result of nonuniform distribution of electron density and create a fleeting, temporary dipole called an instantaneous dipole
what does a larger dipole moment mean?
stronger intermolecular force, which means a higher boiling point
what are London dispersion forces?
forces that arise out of dipoles that are induced by neighbouring molecules
what are ion-dipole interactions?
coulombic attractions between ions (+ or -) and polar molecules
the magnitude of ion-dipole interactions depend on the ________ and the _______ of the ion
charge; size
the magnitude of ion-dipole interactions depend on the _________ and _______ of the polar molecule
dipole moment; size
what is surface tension?
the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid by a unit area
a liquid with strong intermolecular forces has a ______ surface tension
high
what is viscosity?
measure of a liquid’s resistance to flow
what does a higher viscosity mean?
stronger intermolecular forces
vapour pressure increases with ___________
temperature
the ____________ of intermolecular forces is what determines whether the particles that make up a substance are a gas, liquid, solid
magnitude
what is a van der Waals force?
attractive forces between atoms or molecules in a pure substance and they include dipole-dipole interactions, including hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces
what is interesting about hydrogen bonding?
molecules capable of hydrogen bonding have a higher boiling point than expected based on molecular size trends
what does the magnitude of disperson forces depend on?
it depends on how easily the molecule’s electrons can be polarized and the polarizability of a molecule increases with increasing number of electrons
what is vapor pressure?
pressure of gas above liquid
what is special about substanes with high vapor pressures at room temperature?
they are said to be volatile (able to shift from the liquid to gas phase quickly)
higher vapor pressure indicates _________ intermolecular forces
weak
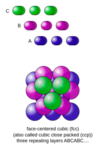
what is a crystalline solid?
it possesses rigid and long-range order; it’s atoms, molecules, or ions occupy specific positions
what is the arrangement of the particles in a crystalline solid and what does it depend on?
it is called the lattice structure and it depend on the nature and size of the particles involved
what is a unit cell?
a unit cell is the basic repeating structural unit of a crystalline solid