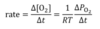chapter 14 Flashcards
(15 cards)
what is the half life for zeroth order reactions?

what is the half-life equation for first order reactions?

what are the units for order reactions?

what is the half life equation for second order reactions?
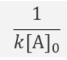
what is the collison theory?
the reaction rate is directly proportional to the number of molecular per second

what is an elementary reaction?
one that occurs in a single collison of the reactant molecules
what is molecularity of an elementary reaction?
number of reactant molecules involved in the collision
- unimolecular
- bimolecular
- termolecular
what is necessary for a reaction to be catalyzed?
sufficient energy and proper orientation of the molecule
what is a catalyst?
speeds up a reaction, appears in an early step and then is present at the end and is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being consumed
what is the potential energy profile for a two-step reaction in which the first step is rate determining?
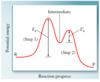
what does a catalyst do?
lower the activation energy

what is homogenous catalysis?
reactants and the catalyst are dispersed in a single phase, usually liquid. it is more advantageous than heterogenous catalysis since it can be carried out under atmospheric conditions
what is heterogenous catalysis?
reactants and catalyst are in different phases
what is average rate?
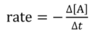
what is the rate in gas pressure?
O2 can be substituted with other gases and T has to be in kelvins