Chapter 12: Soft Tissue Tumors Flashcards
(237 cards)
what is the treatment of a palisaded encaspulated neuroma?
surgical excision
are most melanotic neuroectodermal tumors of infancy benign or malignant?
benign
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia is a condition related to what 3 things?
- ill-fitting denture
- poor denture hygiene
- wearing a denture 24 hours/day
what is the appearance of peripheral ossifying fibroma?
nodular mass, usually originating from the dental papilla

inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
___% of peripheral ossifying fibromas recur. why?
15%, usually because the base of the lesion was not removed

giant cell fibroma

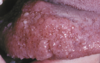
multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B
notice the multiple mucosal neromas on the tongue and the bilateral neuromas of the commissural mucosa

palisaded encapsulated neuroma
___ of neurofibromatosis type I is pathognomonic
plexiform variant
feels like a bag of worms

sturge-weber angiomatosis
ipsilateral hypervascular changes
are pyogenic granulomas more common in males or females?
- females
- frequently occurs in pregnant women, most commonly in the 1st trimester
- some regress after pregnancy
leptomeningeal angiomas are typically associated with a ___, and may result in mental retardation or ___
- convulsive disorder
- contralateral hemiplagia (one-sided paralysis)
lipomas are the most common ___ neoplasm
mesenchymal
more common on the trunk
is the mechanism by which tumors can spread to the oral cavity well understood?
no

peripheral giant cell granuloma
notice the bluish color
what are the two types of rhabdomyomas?
- adult
- 70% in adult men
- nodular mass most commonly occurring int he pharynx and floor of mouth
- fetal
- young male patients
- predilection for the face
endemic (african) kaposi’s sarcoma has 4 subtypes. what are they?
- benign nodular (similar to classic)
- aggressive
- florid
- lymphadenopathic (children)
what are the diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis type I and how many do you need for a positive diagnosis?
need 2 or more for a positive diagnosis
- six or more cafe au lait macules
- “coast of california”
- two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma
- freckling in the axillary region (crowe’s sign)
- optic glioma
- two or more iris hamartomas (lisch nodules)
- osseous lesion such as sphenoid dysplasia
- first degree relative with neurofibromatosis type I
what is the treatment for fibromas?
conservative surgical exision

port wine stain aka nevus flammeus characteristic of sturge-weber angiomatosis
describe the classic type of kaposi’s sarcoma
- 80% in older men
- italian, jewish, or slavic descent
- multiple, asymptomatic blue-purple macules on the lower extremities which grow into nodules
___ is reactive hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue in response to local irritation or trauma
fibroma
what is the treatment of peripheral ossifying fibroma?
excision down to periosteum and scale adjacent teeth