Chapter 15: The Lung - Congenital through Obstructive Flashcards
(127 cards)
Except for the vocal cords, the entire respiratory tree is lined by what type of epithelium?
Pseudostratified, tall, columnar, ciliated epithelium

Bronchia mucosa contains population of neuroendocrine cells with neurosecretory granules containing which factors?
- Serotonin
- Calcitonin
- Gastrin-releasing peptide (bombesin)
Numerous mucus-secreting goblet cells and submucosal glands are dispersed throughout the walls of which parts of the respiratory tree?
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- NOT the bronchioles

What are 2 functions of the Type 2 pneumocytes of the alveolar epithelium?
- Produce surfactant
- Repair of alveolar epithelium by giving rise to type 1 pneumocytes
Pulmonary hypoplasia occurs in utero and what are 2 major causes?
- Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
- Oligohydramnios
Foregut cysts are most often located where in the lungs and which classification/type is most common?
Treatment?
- Hilum or middle mediastinum
- Bronchogenic = most common
- Excision = curative!

Pulmonary sequestration refers to a discrete area of lung with what 2 features?
- Lacks any connection to the airway system
- Has abnormal blood supply arising from aorta or its branches

Congenital pulmonary adenomatoid malformations (CPAM/CCAM) are caused by what?
“Arrested development” of pulmonary tissue –> formation of intrapulmonary cystic masses WITH connection to tracheobronchial airways and pulmonary vasculature

Via which imaging modality can congenital pulmonary adenomatoid malformations be detected?
Fetal ultrasound
Congenital pulmonary adenomatoid malformations can be deadly due to what complications?
- Hydrops or pulmonary hypoplasia
- Can get infected later in life
Extralobar pulmonary sequestrations most commonly come to attention in infants how?
- As mass lesions
- Associated w/ other congenital anomalies

When do intralobal pulmonary sequestrations typically present and are often due to what?
- Older children/adults
- Due to recurrent localized infection or bronchiectasis

Atelectasis is a reversible disorder, except in cases caused by what?
Contraction atelectasis
What are the 3 main types of acquired atelectasis and what is each caused by?
- Resorption due to complete obstruction of airway (mucus plugs)
- Compression due to accumulation of material or air within pleural cavity (i.e., transudate/exudate/blood or pneumothorax)
- Contraction due to fibrosis or restrictive processes in pleura preventing full lung expansion

Which type of acquired atelectasis causes the mediastinum/trachea to shift toward the affected lung; which type causes a shift away?
- Resorption —> mediastinum shifts toward affected lung
- Compression –> mediastinum shifts away from affected lung
Which type of acquired atelectasia occurs in the setting of asbestosis?
Contraction atelectasis
Hemodynamic pulmonary edema is due to an increase in what; most commonly occuring in what setting?
↑ hydrostatic pressure –> left-sided CHF
What is the histological appearance of of the alveolar capillaries in hemodynamic pulmonary edema?
Engorged, and an intra-alveolar transudate appears as finely granular pale PINK material

Where does fluid accumulate initially in pulmonary edema due to hydrostatic pressure being greatest in these sites (dependent edema)?
Basal regions of the lower lobes
List 4 causes of decreased oncotic pressure, which cause “leaking out” and pulmonary edema?
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Liver disease
- Protein-losing enteropathies
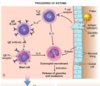
List some of the etiologies which can cause direct injury to the alveolar wall leading to pulmonary edema?
- Infections: bacterial pneumonia
- Inhaled gases: high [O2] and smoke
- Liquid aspiration: gastric contents; near drowing
- Radiation
What are 2 causes of pulmonary edema of undetermined origin?
- High altitude
- Neurogenic (CNS trauma)
In long-standing pulmonary congestion (i.e., mitral stenosis), hemosiderin-laded macrophages are abundant, and what is the gross morphology of the lungs?
Soggy lungs become firm and brown (brown induration)
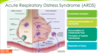
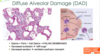
When the edema associated with pneumonia fails to stay localized and instead becomes diffuse alveolar edema what fatal condition may this lead to?
ARDS