Chapter 5 - The Nervous, Muscular, and Skeletal Systems Flashcards
After completing this deck, the fitness professional will be able to outline the basic structure and function of the nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems and identify the effects exercise has on each of those systems. (78 cards)
What is another name for a fast-twitch muscle fiber?
Type 2 Muscle Fiber
Type 2 muscles tend to have less blood supply and mitochondria than type 1 muscles. They are larger in size but fatigue faster than type 1.
What is the functional cell of the nervous system?
Neuron

What is a sesamoid bone?
Small bone imbedded in a joint capsule or membrane of a joint
An example of a sesamoid bone is the patella
Define
Nervous System
A group of cells that work together to create a network used for communication within the human body.
For more information about the nervous system and its function, click here!
Define
Afferent pathway
The sensory pathway that relays information from the body to the central nervous system.
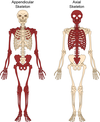
What parts of the body make up the appendicular skeletal system?
Upper and lower extremities including the shoulder and pelvic girdle
What are the three layers of fascia in a muscle, from superficial to deep?
- Epimysium (covers entire muscle)
- Perimysium (covers a fascicle)
- Endomysium (Covers a muscle fiber)
Why is elastin found in ligaments?
To provide flexibility and elastic recoil
80% of joints in the body are what kind of joint?
Synovial.
Define
Motor Function
The ability of the nervous system to respond to changes in the environment, both internally and externally.
Motor is also known as efferent.
The autonomic nervous system can be split into what two divisions?
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic
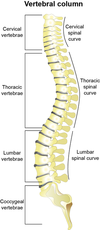
What are the largest vertebrae in the vertebral column?
Lumbar.
The 5 lumbar vertebrae are the last of the vertebrae and are responsible for supporting most of the body weight.
What are some of the different kinds of processes in the skeletal system?
- Process
- Condyle: forms the attachment points for the knee joint and can be found on the bottom of the femur and the top of the tibia
- Epicondyle: forms the attachment points for the elbow joint and can be found at the bottom of the humerus
- Tubercle: form the attachment points for the shoulder and are found at the top of the humerus
- Trochanter: form the attachment points for the hip joint and are found at the top of the femur
What is the functional unit of the muscular system?
Sarcomere
Several myofibrils together will form what?
A Muscle fiber
True or False
Bones are alive.
True.
Bone is made of both living and nonliving materials.
What are the steps in an excitation-contraction coupling?
- Nerve impulse begins in the CNS and travels down the neuron to the neuromuscular junction
- Acetylcholine is released and crosses the synapse and reaches the muscle
- The nerve impulse travels to the sarcoplasmic reticulum and causes a release of calcium
- Calcium stimulates a chain of events that results in the myosin heads attaching to actin
- Myosin head pulls on actin and then releases and repeats, causing a shortening of the sarcomere and the shortening of a muscle.
For more information, click here!!
What neurotransmitter is used to initiate a muscle contraction?
Acetylcholine
Define
Mechanoreceptor
Specialized structures that respond to mechanical forces, such as touch and pressure.
Define
Motor unit
A motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates with.
Define
Epiphysis
The ends of a long bone

What are the classifications of synovial joints?
- Gliding (ex. wrist)
- Condyloid (ex. fingers)
- Hinge (ex. elbow)
- Saddle (ex. thumb)
- Pivot (ex. neck)
- Ball and Socket (ex. shoulder)
What is the scientific name for a mature bone cell?
Osteocyte
What are some characteristics of a long bone?
- Long cylindrical shaft
- Irregular shaped and wide ends
Examples of long bones include the fibula or femur.