Chapter 6 & 7 Flashcards
(39 cards)
What do price controls do?
Attempt to set prices through government involvement in the market
What is a price ceiling?
A legally established maximum price for a good or service
What happens when a binding price ceiling is established?
- The quantity demanded by consumers rise as price drops (law of demand)
- The quantity supplied decreases as producers are less willing to sell (law of supply)
- This results in a shortage
- A shortage is usually corrected by the market by an increase in price, which is not possible because of the price ceiling
What are the unintended consequences that follow a price ceiling being established?
- Smaller quantity of good supplied
- Black markets are established
When are price ceilings non-binding?
When the price ceiling is above the equilibrium price (still regulated by supply and demand)
When are price ceilings binding?
When they are lower than the price determined by the market
Where is the black market price when a price ceiling is established?
Quantity supplied at shortage, vertically follow to demand curve
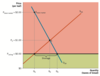
What are the effects of price ceilings in the long run in reference to supply and demand?
- Supply becomes more elastic as producers will produce less when prices are low
- Demand becomes more elastic because consumers will want to buy more when prices are low
- Greater shortage
Describe the graph of rent control (imposing price ceiling)

Describe the graph when price gouging laws are put in place

What are the unintended consequences that follow the establishment of a price floor?
- A smaller demand for the good
- Black market establishment
When are price floors non-binding?
Lower than the equilibrium price determined by market
When are price floors binding?
When it is higher than the price determined by market
Where is the black market price when a price floor is established?
Quantity supplied, vertically follow to demand curve

What are the effects of price floors in the long run?
- Supply becomes more elastic as more producers are more willing to sell at high prices
- Demand becomes more elastic as consumers will find substitutes for the good
- Greater surplus
Describe the graph when minimum wage laws are put in place

What are externalities?
- The costs or benefits of a market activity that affect a third party
- Type of market failure
When does a market failure occur?
When there is an inefficient allocation of resources in a market
What are social costs?
The sum of the internal costs and external costs of a market activity
What are internal costs?
The costs of a market activity paid only by an individual participant
What are external costs?
The costs of a market activity imposed on people who are not participants in that market
When does a third-party problem occur?
When those not directly involved in a market activity experience negative or positive externalities
What is the social optimum?
The price and quantity combination that would exist if there no externalities
How are negative externalities corrected?
Government requires the firm to internalise an externality and account for the external costs to society that occur as a result of its actions
- overproduction
eg. taxes


