Chapter 9 Flashcards
(25 cards)
When do Competitive Markets exist?
When there are so many buyers and sellers that each one has only a small impact on the market price and output
What are the characteristics of a highly competitive market?
Similar goods
Many sellers
Low barriers of entry
Price taking
Shkn me bld pns
Who is a price taker?
- Someone who has no control over the price set by the market
- Takes the price determined by the overall supply and demand conditions that regulate the market
Why is a market structure of perfect competition most beneficial to society?
Creates the maximum combined consumer and producer surplus
What is the Profit Maximising Rule?
Profit maximisation occurs when a firm chooses the quantity of output that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost (MR = MC)
At what point should production stop?
Production should stop at the point at which profit opportunity no longer exists and losses have not yet occurred (MR = MC)
What is Marginal Revenue?
Change in total revenue a firm receives when it produces one additional unit of output
What is the two-step process in determining the most profitable output?
- Locate the point at which the firm will maximise its profits: MR=MC
- Follow the point to the x-axis GRAPH

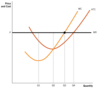
How is profit determined in a competitive firm?
Profit = (price - ATC [along the dashed line at quantity Q]) x Q
- The ATC of producing Q units can be found at the intersection between the lines

When should a firm shut down?
- Firms should continue operating if the variable costs can be covered (as some money may also cover the fixed costs)
- However, if it cannot cover its variable costs then it should shut down
- When MR falls below the AVC curve
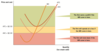
What is the firm’s Short-Run Supply Curve and where is it 0?
- The marginal cost curve is the firm’s short run supply curve as long as the firm is operating.
- Below the minimum point on the AVC curve (where the business would shut down), the short run supply curve is vertical at a quantity of zero.

What is the firm’s Long-Run Supply Curve and when is it 0?
- All costs are variable in the long run (AFC does not exist)
- The firm’s long-run supply curve does not exist when the firm cannot cover its total costs of production (ATC)
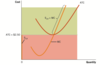
When should a firm shutdown in the Long-Run?

What is the Short-Run Market Supply Curve?
- The sum of the supply curves of all firms in the market

Where does the Long-Run Supply Curve exist?
Where P = min.ATC (horizontal line)
Why is the Long-Run Supply Curve horizontal at min.ATC?
- Existing firms decide whether to enter and exit a market based on incentives (profits)
- When profits exist, firms would enter the market, increasing the supply, adjusting price to decrease to P = min.ATC
- When losses exist, firms would leave the market, decreasing supply, adjusting prices up to P = min.ATC
- At zero economic profit, no firms are incentivised to enter or exit the market

Why are firms happy with zero economic profit?
Both explicit and implicit costs have been covered (includes the highest valued alternative)
Where do the short-run market supply curve and the short-run market demand curve intersect in long-run equilibrium?
Where P = min.ATC in the firm’s curves

When is the firm in short-run profits?
The short-run supply curve and the short-run demand curve intersect above the long-run supply curve, the price would be higher than the min. ATC
When is the firm in short-run losses?
The short-run supply curve and the short-run demand curve intersect below the long-run supply curve, the price would be lower than the min. ATC
What is the short-run adjustment to a decrease in demand?
A decrease in demand causes price to fall in the market
- Because the firm is a price-taker in a competitive market, the price falls to P2
- The intersection between MR2 and MC occurs at Q2, which is lower than minimum ATC
- The firm incurs a short-run loss (Market sets price for firm)

What is the Long-Run adjustment to a decrease in demand?
- Due to the decrease in price, firms exit the market, decreasing the supply curve until the price returns to long-run equilibrium (C), but at a lower level of output
- Price is restored in the individual firm and the firm starts earning zero economic profit again

When may the long-run supply curve not be horizontal and why?
Can slope upwards due to:
- bidding for limited resources
- increasing opportunity cost for labor
What are sunk costs?
Unrecoverable costs that have been incurred because of past decisions