Chapter 8 Flashcards
(38 cards)
How is accounting profit calculated?
Profit (Loss) = Total Revenue - Explicit costs
What is Total Revenue?
The amount a firm receives from the sale of goods and services
What are explicit costs?
The amount a firm spends to produce and/or sell goods and services
How is Economic Profit calculated?
Economic Profit = total revenues - (explicit costs + implicit costs)
= accounting profit - implicit costs
What are explicit costs?
Tangible out of pocket expenses
What are implicit costs? Give an example.
The costs of resources already owned, for which no out-of-pocket payments are made.
eg. opportunity costs
How does accounting profit compare to economic profit?
Economic profit is always less than accounting profit
What is the production function?
The relationship between the inputs a firm uses and the output it creates
What are inputs?
A resource used in the production process to generate output
What are the three primary factors of production?
Labor, land and capital (LLC)
What are outputs (in relation to the production function)?
The product the firm creates
What is marginal product?
The change in output associated with one additional unit of input
When does the point of diminishing marginal product occur?
When successive increases in inputs are associated with a slower rise in output.
- Firms should continue production as long as the revenue from output is more than the costs of input
Why does diminishing marginal product occur?
The firm is fixed in the short run and inputs are fully utilised
The gains from specialisation slowly decline
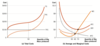
Describe the graph of marginal product

How do we calculate average total costs (ATC)?
= AVC + AFC = Total cost / Quantity (Q)
Why does the ATC rise?
Eventually, the increases in variable costs overwhelm the cost savings achieved by spreading fixed cost across more production
What are variable costs?
Costs that change with the rate of output
How do we calculate average variable costs?
TVC / Quantity (Q)
What are fixed costs (a.k.a overhead)?
Unavoidable costs that do not vary with output in the short run
How do we calculate average fixed costs?
TFC / Quantity (Q)
What happens to average fixed costs when output increases?
AFC declines
What is marginal cost?
The increase in cost that occurs from producing one additional unit of output
How is marginal costs calculated?
Change in total cost / Change in Quantity