Day 3: return of the king Flashcards
(32 cards)
Define tachycardia
Define bradycardia
tachycardia: a heart rate over 100bpm
bradycardia: a heart rate under 60bpm
What are DNA and RNA?
DNA - found only in the nucleus
The genetic information of the organism
RNA - found in the cytoplasm of the cell
Is a temporary copy of the DNA which is used by ribosomes to “print” proteins
Label each bacterial colony shape


The four most common causes of dementia are
Alzheimer’s disease
Lewy body dementia
Frontotemporal dementia
Vascular dementia
How do they affect the brain?
Alzheimer’s disease: beta-amyloid proteins build up and cause inflammation of the brain
Lewy body dementia: alpha-synuclein proteins build up and cause inflammation of the brain
Frontotemporal dementia: Caused by being hit in the head which causes “tau” proteins to build up leading to inflammation
Vascular dementia: poor blood supply to the brain
What is the main difference between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells don’t have a defined nucleus
Anxiety disorders are linked to which part of the brain?
The amygdala
Which sexually transmitted infection results in discharge of lots of puss from the genitals?
gonorrhoea
What is the difference between
dominant and recessive
genes?
Dominant: only one copy of the gene is needed for the trait to be expressed.
Recessive: two copies are needed for the trait to be expressed
What are the target Oxygen sats for a patient with
type 2 respiratory failure (like COPD)
88-92%
Which hormone causes the fight or flight response?
Adrenaline
How do you treat heart failure?
ACE inhibitors
What are the common treatments for anxiety?
(3)
SSRIs (anti depressants)
CBT (cognitive behavioral therapy)
Benzodiazepines
Name each stage of the Septic Six
(BUFALO)

What are the effects of HPV?
(3)
most people have no symptoms
some people develop genital warts
it can also cause cervical cancer
What are the structures of
DNA
RNA

DNA: a long “double helix” shape wrapped around itself
RNA: a short string in a line
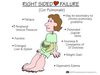
What is left-sided heart failure?
What are the signs and symptoms of left-sided heart failure?
When the left side of the heart grows too large, interfering with the heart’s normal function.
- Difficulty breathing
- Cough
- Cyanosis

Which brain chemical is linked to psychosis?
dopamine
Which immune cells are responsible for killing infected human cells?
T-cells
Which drug prevents vasoconstriction and increases capillary refill time
ACE inhibitors
Which immune cells produce antibodies?
B-cells
also called
plasma cells
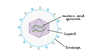
Label this virus (3)

You are escalating a patient to a senior.
What does the SBARD acronym stand for?
Situation
Background
Assessment
Recommendation
Decision
Which structure of the brain is involved in our response to stressful situations?
Amygdala
What is meant by these heart terms?
Preload
Afterload
Cardiac output
Stroke volume
Preload: the initial pressure in the heart before contraction
Afterload: Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction
Cardiac output: The volume of blood pumped in a minute
Stroke volume: The amount of blood pumped in one contraction