DI Midterm Exam Material Flashcards
(142 cards)
T/F: Pneumomediastinum may result in dyspnea
False
If you see an enlargement in this region, what should your top two differentials be?

Tracheobronchial lymphadenopathy and Left atrial enlargement

T/F: Ring Shadows (donuts) are often associated with a bronchial pattern
True
Bronchial pattern: donuts and tram lines
T/F: Hepatic veins have a hyperechoic wall on ultrasound
False
Hepatic veins have an isoechoic wall
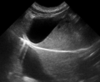
This is a sagittal image of the left kidney. Which side is cranial?

That one.

What view would be best for evaluating lesions in the right lung lobes?
Left Lateral
- In small animals, lung lesions generally are detected best in the non-dependent lung because the “up” lung is better aerated and therefore provides better contrast of lesions*
- Keep in mind, other lesions (not in the lung) generally are best seen on the “down” side because they are not distorted by magnification*
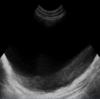
What echocardiographic modality would you use to measure wall thickness during systole and diastole?
M Mode
Name the MR sequence that nulls signal from free fluid (i.e. CSF):
FLAIR
_FL_uid _A_ttenuated _I_nversion _R_ecovery
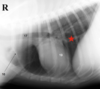
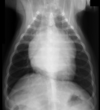
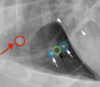
Is sternal lymphadenopathy present in this patient?

Yes.
Note the enlargement of the sternal lymph node
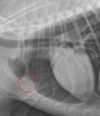
T/F: Ascites is commonly associated with mitral valve insufficiency
False
That is false
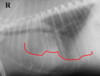
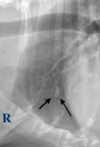
Is the circled lesion more likely in the lung or the mediastinum?

Lung
Note the acute angle to the body wall. If the lesion was in the lung you would not have such an acute angle
With which radiographic view is mediastinal shift best visualized?
VD/DV
Doppler measurements should be taken with the patient in ______ lateral recumbency
LEFT
If you see a “bow-legged cowboy sign” on a DV view, what is your DDx?

left atrial enlargement

Identify the lymphatic structure indicated by the number 3:

Tracheobronchial

T/F: Diaphragmatic hernias cause caudal displacement of the gastric axis
False
Diaphragmatic hernias cause cranial displacement of the gastric axis
Long-axis left ventricular outflow view.
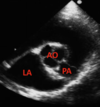
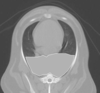
Identify the structure indicated by the number 2

right atrium

T/F: An overexposed radiograph is too light
False
An overexposed radiograph is too dark. Either kVp or mAs is too high.
T/F: If you suspect a lesion in the right lung of a dog, a left lateral thoracic radiograph should be made
True
What diagnostic imaging modalities might you use if you suspect a diaphragmatic hernia?
Radiographs, Ultrasound, Barium Study
RUB the hernia…
…creep
T/F: Atelectasis is associated with normal to increased size of the lung lobe
False
- Atelectasis is associated with decreased size of the lung lobe*
- Consolidation is associated with normal to increased size of the lung lobe*
This presentation is most often associated with _______ insufficiency

mitral insufficiency
Turbulent flow (regurgitation); often bright and a mixture of colors
T/F: Mammary adenocarcinomas are typically associated with mediastinal lymphadenopathy
False

T/F: Tracheobronchial lymphadenopathy is an example of a cranioventral disease
False
Tracheobronchial lymphadenopathy is an example of a dorsal disease