Diastology Flashcards
(121 cards)
Define diastolic dysfunction
- Inability of the ventricle to fill to an adequate end-diastolic volume at normal pressure
- abnormality of LV diastolic:
- distensibility
- filling
- relaxation
LV diastolic dysfunction is usually the result of this:
- impaired LV relaxation with or without reduced restoring forces (and early diastolic suction)
- increased LV chamber stiffness
Both of which lead to increased cardiac filling pressures
Describe the algorithm differentiating CP and Restrictive Cardiomyopathy?

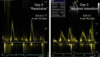
How will pulmonary venous Doppler flow pattern immediately change in the case of left atrial stunning (e.g. after cardioversion for persistent A-fib)?
A decrease of the systolic filling fraction, particularly S1

Define LV filling pressure
Can refer to:
- mean PCWP (which is an indirect estimate of LV diastolic pressures)
- mean left atrial pressure (LAP)
- LV pre-A pressure
- mean LV diastolic pressure
- LV end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP)
What is the diagnosis in patient with:
- Normal systolic function
- PCWP: significant V-waves
- Echo: no evidence of MR
Loss of left atrial reservoir function
or
severely decreased left atrial compliance
61 year old male with PMH HTN with complaints of exercise intolerance.
- LFT’s normal
- HR 60 bpm
- LVEF normal, mild LVH
What is the diagnosis? Next step?

-
Diastolic stress test
- Normal myocardial relaxation –> E/e’ will remain unchanged because both E and e’ velocities increase proportionally
- Impaired myocardial relaxation –> increase in e’ is much less than that of E –> E/’e increases

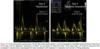
When performing PW Doppler imaging in the A4C view to acquire mitral annular velocities, where should the sample volume be positioned?
At or 1 cm within the septal and lateral insertion sites of the mitral leaflets
- Should be adjusted as necessary (usually 5-10 mm) to cover the longitudinal excusion of the mitral annulus in both systole and diastole
What are supportive findings of CP with mixed mitral medial e’ (6-8 cm/s) in assessment of CP vs. RC?
-
Annulus reversus
- Mitral lateral e’ < medial e’
- Most likely constriction if present
- Hepatic vein expiratory end-diastolic reversal velocity / forward flow velocity = > 0.8
- definitely constriction if present
What are the elements of a basic diastolic function assessment?
- Left atrial volume index
- Mitral inflow Doppler
- Mitral annular tissue doppler (medial and lateral)
- medial is sufficient in most instances, also easier to align
- Right ventricular systolic pressure
What is two echo machine adjustment that should be made when obtaining annular velocities?
- Doppler spectral gain settings
- usually automatic
- velocity scale should be set at ~ 20 cm/s above and below the zero-velocity baseline
- lower settings may be needed in severe LV dysfunction
- Minimal angulation - < 20 degrees
Describe the findings of Grade II diastolic dysfunction
- LV relaxation - impaired
- LAP - Elevated
- Mitral E/A ratio - > 0.8 - < 2
- Average E/e’ ratio - 10-14
- Peak TR velocity (m/s) - > 2.8
- LAVI - Increased

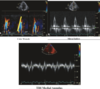
What is the best way to estimate LV filling pressures in A-fib?
What indicates elevated LV filling pressures?
- E/e’ ratio
- E/e’ > 11 –> LVEDP > 15 mmHg
Define LV untwisting
-
Major determinant of the isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT)
- measurable manifestation of elastic recoil
- energy generated by helically oriented fibers and stored in the heart’s elastic tissue during systole is released before end-systole
- creating early diastolic suction
- filling the LV for the next cardiac cycle
What is second step in assessment of CP vs. RC?
Ventricular interdependence (with respiration)
- No –> suspicion still high –> further imaging or cardiac cath
- Yes –> Mitral medial e’
What mitral deceleration time is associated with elevated LV filling pressures?
< 150 ms in the presence of LV dysfunction
What is the best two-dimensional (2D) and doppler echo finding to differentiate restrictive cardiomyopathy from constrictive pericarditis?
Early diastolic mitral annular velocity
- mitral medial e’ velocity > 8 cm/s
- normal mitral e’ velocity (in patient with heart failure) –> CP
What is the optimal sample volume size in PW Doppler assessment:
- Mitral valve inflow
- Pulmonary vein doppler flow
- 1-3 mm at mitral valve tips
- 2-3 mm placed > 0.5 cm into pulmonary vein
What is first step in assessment of CP vs. RC?
Mitral inflow E/A > 0.8
+
Dilated IVC
- No –> Constriction / Restriction unlikely
- Yes –> Next step
Describe the findings in Grade III diastolic dysfunction
- LV relaxation - impaired
- LAP - Elevated
- Mitral E/A ratio - > 2
- Average E/e’ ratio - > 14
- Peak TR velocity (m/s) - > 2.8
- LAVI - Increased

Describe the diagnosis

Restrictive cardiomyopathy

What deceleration time of the pulmonary venous diastolic velocity indicates elevated LV filling pressures?
< 220 ms
Describe pulmonary venous Doppler flow pattern:
AR wave

- AR wave
- atrial flow reversal velocity and duration
- influencenced by LV late diastolic pressures, atrial preload, LA contractility

What are supportive findings of RC in assessment of CP vs. RC?
- DT < 150 ms
- IVRT < 50 ms
- PV Systolic Fraction < 40%
- E/e’ > 15
- LAVI > 48 mL/m2