Diuretics - Potassium-sparing (aldosterone antagonist) Flashcards
(27 cards)
What are diuretics?
1 - drugs that increase water, Na+ and Cl- excretion
2 - drugs that decrease water, Na+ and Cl- excretion
3 - drugs that increase water, K+ excretion
4 -drugs that decrease water, K+ excretion
1 - drugs that increase water, Na+ and Cl- excretion
- reduce fluid retention
Where in the kidneys is blood filtered to form the filtrate?
1 - efferent arteriole
2 - afferent arteriole
3 - glomerulus
4 - juxtaglomerular
3 - glomerulus

Once the filtrate is formed from the glomerulus, what happens to the fluid as it move through the tubules and out of the collecting duct as urine?
1 - only glucose is reabsorbed
2 - Na+ and K+ only are reabsorbed
3 - lots of ions and fluids are reabsorbed
3 - lots of ions and fluids are reabsorbed
- H2O, ions (K+, Na+, Cl-)
- what is left is urine

Where are ions mainly re-absorbed in the renal system?
1 - loop of henle
2 - distal convoluted tubule
3 - proximal tubule
4 - collecting duct
3 - proximal tubule
- location of most diuretics actions
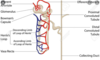
Water passively follows ion re-absorption in the distal tubules of the renal system, which ion specifically does it follow?
1 - Na+
2 - K+
3 -Cl-
4 - HCO3-
1 - Na+
- due to osmosis (H2O dilutes Na+ in blood)
Labels the parts of the renal tubules using the labels below:
1 - loop of henle
2 - distal convoluted tubule
3 - proximal tubule
4 - collecting duct

1 - proximal tubule
2 - loop of henle
3 - distal convoluted tubule
4 - collecting duct

In the distal convoluted tubules there are principle and alpha cells. Which of the following transporter is NOT typically present on the principle cells?
1 - Na+/K+ATPase
2 - H+ ATPase
3 - Epithelial Na+ channel
4 - ATP dependent K+ channel
2 - H+ ATPase
- Na+/K+ATPase = moves 2Na+ back into interstitium and then blood
- Epithelial Na+ channel = reabsorbes 1 Na+
- ATP dependent K+ channel = pumps 1 K+ ion into lumen

In the distal convoluted tubules there are principle and alpha cells. Which of the following transporter is NOT typically present on the alpha cells?
1 - Na+/K+ATPase
2 - H+ ATPase
3 - Epithelial Na+ channel
4 - H+/K+ ATPase
3 - Epithelial Na+ channel

Looking at the image below of the principle and alpha cells located in the distal convoluted cells, which of the following are the functions of the principle cells in a normal functioning kidney?
1 - retain Na+ through the Epithelial Na+ channel
2 - excrete K+ through the ATP dependent K+ pump
3 - reabsorb 3 Na+ into blood and excrete 2 K+ into principle cells through the Na+/K+ ATPase pump
4 - all of the above

4 - all of the above

Looking at the image below of the principle and alpha cells located in the distal convoluted cells, which of the following are the functions of the alpha cells in a normal functioning kidney?
1 - retain 1 K+ form lumen and excrete 1 H+ into the lumen through the H+/K+ ATPase
2 - excrete H+ through the ATP dependent H+ pump
3 - reabsorb 3 Na+ into blood and excrete 2 K+ into alpha cells through the Na+/K+ ATPase pump
4 - all of the above

4 - all of the above

What is the normal function of aldosterone?
1 - inhibits Na+ reabsorption
2 - inhibits K+ reabsorption
3 -Increases Na+, K+ and H2O reabsorption
4 - decreases Na+, K+ and H20 reabsorption
3 - Increases Na+, K+ and H2O reabsorption
- binds with mineralcorticoid receptors on the intercalated cells in the distal tubules
- aldosterone diffuses into the cell and binds to mineralcorticoid receptor forming complex
- the complex enters nucleus and influences DNA causing upregulation of epithelial Na+ channels

Does aldoesterone increase or decrease H+ reabsorption in the distal tubules via the alpha intercalated cells?
- increases secretion into the tubulues
- in exchange a K+ is reabsorbed
- this is important as it ensures there is ample K+ to be exchanged with Na+

Which of the following is the core K+ sparing medication that we need to be aware of?
1 - Bumetanide
2 - Furosemide
3 - Spironolactone
4 - Bendroflumethiazide
3 - Spironolactone
Spironolactone is the core K+ sparing medication that we need to be aware of. Which 2 locations in the renal tubules does Spironolactone act on?
1 - loop of henle
2 - distal convoluted tubule
3 - proximal tubule
4 - collecting duct
2 - distal convoluted tubule
4 - collecting duct

Spironolactone is the core K+ sparing medication that we need to be aware of. Spironolactone acts on the cortical collecting tubules namely the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct. Specifically, Spironolactone acts on the alpha intercalated and principal cells. What is the main function of the intercalated cells?
1 - reabsorb K+ and remove Na+
2 - reabsorb Na+ and Cl-
3 - reabsorb K+
4 - reabsorb Na+ and remove K+

4 - reabsorb Na+ and remove K+

What is the mechanism of actoion of the potassium sparing diuretic spirolactone?
1 - inhibits Na+/K+ ATPase
2 - inhibits Na+/K+/Cl co-transporter
3 - inhibits H+/K+ co-transporter
4 - inhibits aldoserone receptor
4 - inhibits aldoserone receptor
- increase Na+ and H2O excretion
- decrease K+ and H+ excretion
Why is the potassium sparing diuretic spirolactone indicated and the 1st line drug in ascites and oedema due to liver cirrhosis?
1 - reduces stress on liver
2 - redcues SVR
3 - increases urine output and therefore reduces fluid retention
4 - decreases portal hypertension
3 - increases urine output and therefore reduces fluid retention
Why is the potassium sparing diuretic spirolactone indicated chronic heart failure?
1 - increases SVR
2 - redcues SVR
3 - reduces workload of heart
4 - decreases portal hypertension
3 - reduces workload of heart
Does the potassium sparing diuretic spirolactone help in primary hyperaldosterone?
- yes
- it is indicated in this group of patients while they await surgery
Which of the following is NOT typically an adverse event of the potassium sparing diuretic spirolactone?
1 - hypernatraemia
2 - hyperkalaemia
3 - gynaecomastia
4 - liver impairmenr and jaundice
5 - Stevens-Johnson syndrome (T-cell mediated hypersensitivity)
1 - hypernatraemia
- gynaecomastia is caused by a decrease in testosterone levels
Spirolactone can cause hyperkalaemia, which can lead to cardiac abnormalities. Which of the following does not typically occur on an ECG n patients with hyperkalaemia?
1 - prolongation the PR interval
2 - prolongation the QRS interval
3 - loss of P wave
4 - ST segment elevation
4 - ST segment elevation
Spirolactone can cause hyperkalaemia, which inturn does what to the resting membrane potential?
1 - decreases resting membrane potential
2 - increases resting membrane potential
3 - no effect
1 - decreases resting membrane potential
- this essentially means that it is easier for muscles to contract, which can result in muscle pain and fatigue
The potassium sparing diuretic spirolactone should be avoided in all of the following EXCEPT:
1 - patients with hyperkalaemia
2 - patients with impaired renal function
3 - patients with renal insufficiency
4 - patients with hepatic encephalopathy
4 - patients with hepatic encephalopathy
Is spirolactone ok to use in women who are pregnant or breast feeding?
- no
- should be avoided
- evidence to show it can cross the placenta and appear in breast milk


