Embryology: Germ Layers Flashcards
(42 cards)
Label the following image

a. Zygoye
b. fertilized egg
c. Cleavage
d. Morula
e. Blasttula Embryoblast
f. 2 layer embryo

How many weeks after ferlization foes the cell become the blastula/embyoblast? when does the 2 layer embryo form?
- Week 1
- Week 2
when does gastrulation occur?
week 3

what major events happen during this phase of embrology?

Folding, migration, growth, differentiation

Label the diagram
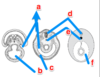
a. coelom
b. yolk sac
c. somatic LPM
d. Nerve tube
e. notochord
f. coelom

Label the diagram of the Bilaminar Germ Disc

- Bilaminar Germ Disc
- Developing Mouth
- Primitive Streak
- Epiblast
- Hypoblast

The epiblast cells migrate through the __________ to form which germ layers
- Primitive Streak
- to form all 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
Label this diagram of gastrulation (3 layer embryo)

- Developing Mouth
- Migrating Epiblast
- Primitive Streak
Is this step gastrulation or neurolation?

gastrulation
no notochord formation
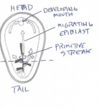
Label this diagraph of neurulation

a. Notochord induces neural folds
b. head
c. tail
d. primitive node
e. primitive streak

Label the following diagram

- Neural Folds
- Future Neural Crest
- Future neural tube

the surface ectoderm becomes the _______
skin
At the end of neuralation ______folding start forming
lateral
label the following diagram

- paraxial mesoderm
- intermediate mesoderm
- somatic laterial mesoderm (L.P.M)
- Splanchnic L.P.M
- Cardiac Tubes
- Notochord Acial Mesoderm
- Coelom

______becomes the surface epithelium and neural tissue
Ectoderm
______becomes the epithelium
endoderm
______becomes all muscles and connective tissues, and some epithelia
mesoderm
Label the following diagram

- neural tube and crest
- paraxial
- Intermediate
- lateral plate: arms (somatic and splanchnic)
- somatic
- splanchnic
- embryonic coelom
- ectoderm
- endoderm tube


This is a cross-section of germ layers as embryonic folding occurs
Label this longitudinal section of the germ layers

- ectoderm
- neuroectoderm
- endoderm
- mesoderm

the head to tail folding that occurs during embryonic folding at week 4 is called________
cephalocaudal folding
What is embryonic folding?
formation of the gut and coelomic cavity
which tissue can arise from all 3 germ layers?
epithelia
connective tissue with the exception of the neural crest arises from _______
mesoderm




