Exam 2 - Fall Flashcards
(143 cards)
scoliosis is a persistent lateral curvature of =
ddx =
> 10 degrees on standing xray
> 10 degrees radiographically by Cobb (L)/Ferguson (R) methods
curvatures in what gender are more likely to progress and produce symptoms?
females
type I dysfx maintained by:
long paraspinal restrictor M
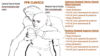
name the scoliosis:

name for direction of ratation: convexity
levo: left scoliosis: convex left
dextro: right scoliosis: convex right
types of scolosis curves: fx v structural
fx: straighten when SB
struct (fixed): does NOT straighten when SB
transitional points of curves
apex:
crossover point:
apex: max rotation – where R mechanics change
crossover point: joining of 2 curves – where SB mechanics changes
*** places were type II SD found
a gorup curve ______ existing spinal kyphosis/lordosis
increases
at a crossover point, the existing AP curve is ________
decreased
fryette’s 2nd principle
SB intro into non-neutral spine, bodies of vert will R to side of concavity (same SB & R)
type ___ lesions should be treated first
II
type II curves are mainted by:
short restrictors: rotatores brevis & intertransversari M
type II SD occurs as a result of
ddx from type I?
trauma/abrupt twisting
type I: chronic
apical type II SD reflect a ________ in AP curves
ex?
increase:
flex @ thoracic
ext @ lumbar
difference of segments above and below apex?

above apex: SB & R in same direction
- upper half of curve behaves as a series of type II dysfx
apex & below: SB & R in opposite directions
progression of idopathic scoliosis & associated pain
begin: fx curve (no pain)
late adolescence: structral ( no pain - able to compensate)
adult–> middle age: segments adjacent to restricted areas become painful due to mechanical stress of compensation
- found @ crossover points above & below fixed curve
classification of scolosis (4)
- reversibility
- severity
- location
- etiology
Classification: Severity of scoliosis
mild: 5-15
mod: 20-45
- >30 should be tx
- >5 degree profession = indication to tx
severe: >50
- >50 compromises respiratory fx
- >70 compromises CV fx
Classification: Location of scoliosis


etiologies of scoliosis
idiopathic: most common
congenital: most of progressive
acquired:
- osteomalacia
- inflammation
- irradiation
- psoas syndrome
- heald leg fx –> short leg
- hip fx/prosthesis –> short leg
what is the most common cause of type I group mechanics?
unequal leg length –> sacral base unleveling
infantile scoliosis
non-wt bearing
due to intra-uterine position: intraosseus occipital dysfx:
- asymmetric compression of condylar parts
- torsion of SBS
- compensatory scoliosis from above downwards
becomes apparent by birth–>age 3
myopathic scolosis is due to
asymmetric strength
musc dystrophy
neuropathic scoliosis is due to
- polio
- cerebral palsy
- spinal tumors
- von recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis (AD)