OMM Exam 3 - Spring Flashcards
(68 cards)
kidneys boundaries:
superior:
inferior:
lateral:
medial:
central:
superior:
- diaphragm
inferior:
- between rib 12 & iliac crest
- L touches rib 11
lateral:
- muscles of ab wall
medial:
- lateral psoas
central:
- QL proximal to 12th intercostal, iliohypogastric & ilioinguinal nerves
referred pain patterns from QL
origin, insertion & action
origin: 12th rib & TPs of L1-L4
Insertion: iliolumbar ligament & posterior iliac crest
action:
- stabilize 12th rib
- lateral flexion unilateral
- extension bilater;

referred trigger points psoas

reanl fascia
anterior:
posterior:
superior:
anterior: pariental peritoneum
psoterior: fascia of QL & psoas, attaches to SC & diaphragm
superior: crus of diaphragm –> ALL
mvmt of kidneys
no ligament or mesentary to anchor, only hilar vessels & urters continuous
downward motion: semifluid perirenal fat & psoas “slide”
upwards: throacic respiration
posterior: standing forces ab muscles contract –> increased intraab pressure –> pushes kidneys posterior
inspiration: down & external rotation
renal ureter referred pain
upper: ASIS anterior to border to rectus abdominis
middle: inguinal ligament anterior to rectus abdominis
lower: suprapubic area –> scrotum/labia
“droped kidney” (3)
nephroptosis: 3cm downwards to internal iliac fossa
associated with constipation
inferior fasical tunnel allows for sliding motion
OMM: nephroptosis
visceral manipulation
posterior:
- exercises to stregnthen abs
- SD: T10-L2
sympathetic innervation:
kidneys:
ureters:
bladder:
kidneys:
- superior mesentaric ganglion: T10-L1
ureters:
- upper: superior mesentaric ganglion: T10-L1
- lower: inferior mesentaric ganglion: L1-L2
bladder:
- inferior mesentaric ganglion: T12-L2
Chapman’s:
kidney:
appendix:
bladder:
prostate:
kidney:
- anterior: ipsilateral 1’ lateral & superior to ubilicus
- posterior: L1
appendix:
- tip of 12th rib
bladder:
- anterior: periumbilical
- posterior: L2
prostate:
- anterior: posterior margin of ITB
- lateral to sacral base @ S1

tx: nephrolithiasis:
inhibit paraspinals T10-L2
address pain before other treatments
htn: omm tx
PNS:
- OA, AA, C2
SNS:
- T1-5 & T10-11
- inferior mesenteric ganglion for renals & adrenals
the bladder is held by what ligaments?
men: puboprostatic
women: pubovesical
a full bladder may ascend to the…
umbilicus via ligament attachments
pelvic diaphragm innervation
pudendal nerve: S2-4
PNS innervation to:
upper ureters:
lower ureters:
bladder:
upper ureters:
- vagus: maintains peristalsis
lower ureters:
- pelvic splachnics (S2-4): increases peristalsis
bladder:
- pelvic splachnics (S2-4): micturition
the pudendal nerve runs in the _______ fossa
ischiorectal
neural controls in micturition
sipnobulbospinal reflex:
- voluntary inhibition of peeing develops at age 2-3
storage phase:
- SNS (T12-L2)
voiding phase:
- initiated vountarily
- PNS (S2-4)
types of incontinence
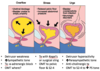
avoid prostate massage when?
bacterioal prostatitis, which could lead to bacteremia
prostatitis: OMM tx
ischiorectal fossa: T12-L2, S2-4
SNS supply to lower GU =
thoracolumbar jxn
Whiplash Grades:
0:
- no complaints
1:
- neck pain
- no physical signs
2:
- neck pain
- decreased ROM/muscle weakness
3:
- neck pain
- decreased ROM/muscle weakness
- sensory deficit
4:
- neck pain
- fx/dislocation
3 phases of whiplash
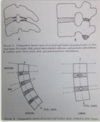
S curve:
- nonphysiologic: F in upper, E in lower
- head lagging behind thorax
- pivotal role in whiplash injury
C curve:
- overall extension
Rebound:
- head contacts head rest