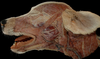
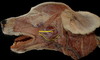
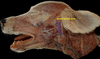
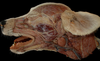
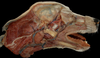
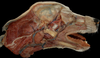
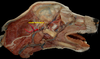
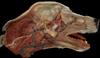
Exam II - Canine Head Flashcards
(89 cards)
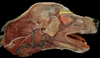
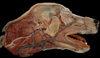
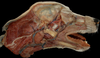
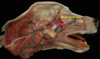
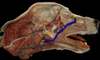
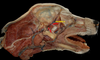
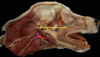
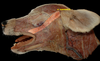
What are the muscles of mastication?
- Masseter
- Temporalis
- Digastricus
- Pterygoid
Which muscle acts to open the mouth?
Which cranial nerve(s) provide innervation to this muscle?
Digastricus m.
Mandibular branch of Trigeminal n (CN V) and Facial n (CN VII)

List the lingual muscles. These muscles are all innervated by which cranial nerve(s)?
- Styloglossus m.
- Hyoglossus m.
- Genioglossus m.
All innervated by CN XII: Hypoglossal n.
Genio- is a prefix meaning _______
*Genio- *is a prefix meaning chin
Example: Geniohyoideus m.
Mylo- is a prefix meaning _______
*Mylo- *is a prefix meaning molar
Example: Mylohyoideus m.
Which thin, flat muscle is the most superficial facial muscle?
Platysma m.

The molar salivary gland is only found in which species?
feline.
The molar salivary gland is on the lingual side of the last lower premolars.

Which lymphatic structure is found rostral to the parotid sliavary gland?
parotid lymph node
Which lymphatic structure straddles the linguofacial vein?
mandibular lymph node
Which lymphatic structure is found between the wing of the atlas and the larynx?
**retropharyngeal lymph node **(medial and lateral)
Name the gland that may be removed unintentionally if you are surgically extracting the thyroid gland
parathyroid gland
_________ laterally connects soft palate to nasopharynx
palatopharyngeal arches laterally connect soft palate to nasopharynx
_________ laterally connects tongue to soft palate
palatoglossal arches: laterally connects tongue to soft palate
What is the purpose of the larynx?
Protects trachea against food aspiration, and aids in breathing and phonation
A rapid narrowing and widening of the glottis by fast twitch muscles in the feline is also known as _________
purring

List the 4 cartilaginous structures of the Larynx
- Epiglottic cartilage
- Arytenoid cartilage
- Thyroid cartilage
- Cricoid cartilage
Which muscle(s) of the larynx tense(s) the vocal fold (phonation)?
cricothyroideus
Which muscle(s) of the larynx open(s) the glottis?
**cricoarytenoideus dorsalis **
Which muscle(s) of the larynx close(s) the glottis?
cricoarytenoideus lateralis
Which muscle(s) of the larynx relax(s) the vocal fold & contrict the glottis?
thyroarytenoideus
The __________ supports the tongue and acts as attachments for lingual mm.; supports the larynx
hyoid apparatus
The opening to the _________ duct is at the 4th premolar
The opening to the parotid duct is at the 4th premolar
The circular opening at the front of the skull where the nose would be is the ___________
nasal aperture
The rostral alar foramen is connected to the caudal alar foramen by a tube called the _________
Alar canal