Final Flashcards
(46 cards)
Name an advantage and disadvantage for tissue engineering of organs / tissues?
Advantage:
no donor/ self donor limitations
disadvantage:
possible immune response
Name a place where adult stem cells can be found
bone marrow
heart
State and describe two components of any basic tissue engineering design
Describe the steps involved in any tissue engineering project
Appropriate cell source must be identified, isolated and produced in sufficient numbers
- Appropriate biocompatible material that can be used as a cell substrate or cell encapsulation material isolated or synthesized, manufactured into desired shape and dimensions
- Cells seeded onto or into material, maintaining function, morphology
- Engineered structure placed into appropriate in vivo site
Distinguish between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells
Embryonic stem cells, found in embryos have not committed to a certain type of tissue
Adult stem cells are tissue specific
Give two disadvantages of organ transplants
there isnt enough organs donated and many die waiting for an organ
What are the advantages of surface modification of biomaterials
biocompatibilty
State three functions of scaffolds?
Function: Delivery of cells to desired sites,
define space for formation,
guide development with appropriate function
Name three requirements for scaffolds for tissue engineering
Be compatible
- Be biodegradable
- Degrade at a rate proportional to the regrowth of the new tissue
Define bioreactor
a system in which conditions are closely controlled to permit or induce a certain behavior in living cells or tissue
Define tissue engineering.
Tissue Engineering is the in vitro development (growth) of tissues or organs to replace or support the function of defective or injured body parts, or the directed management of the repair of tissues within the body (in vivo).
Describe spinner flask bioreactor
Basic bioreactor
- Scaffold suspended at end of needles
- Magnetic stirrer mixes media, while scaffold remain fixed • Typically 120ml, up to 8L, 50-80 rpm
- 50% of medium changed every 2 days
- Mass transfer may not be good enough
What is stent restenosis?
re-narrowing of an artery at the stent
Name three requirements for a potential stent material
- Radial flexibility (necessary during insertion)
- Radial strength
- Appropriate dimensions
What is a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a medical device that uses electrical impulses, delivered by electrodes contacting the heart muscles, to regulate the beating of the heart.
Name 3 cardiovascular medical devices
pacemaker
cardiac stents
ventricular assist device
Describe the process of inserting a stent in a coronary artery
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA), uses a balloon to open a clogged vessel
The PTCA catheter is guided to the required site.
When the balloon is inflated, this presses the plaque against the artery wall and opens up the lumen of the artery to achieve near normal blood flow
What is the primary purpose of a pacemaker?
The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an adequate heart rate, either because of the heart’s native pacemaker is not fast enough, or there is a block in the heart’s electrical conduction system.
What is a Ventricular Assist Device ?
A ventricular assist device (VAD) is a mechanical pump that’s used to support heart function and blood flow in people who have weakened hearts
What important function must a prosthetic hearts perform?
pumping blood
Give two pros and cons for the following heart valve designs: mechanincal, and bioprosthetic
Mechanical
- Advantages – Durability and longevity – Lifespan >25 years
- Disadvantages – Long term anticoagulation therapy – Risk of thrombosis – Component failure
Bioprosthetic
- Advantages – Do not require anticoagulation – Lower risk of thrombosis
- Disadvantages – Progressive risk of valve deterioration – Lifespan 10-15 years – Not an option for young patients
State the four criterion for patient selection for use of an AbioCor artificial heart
Have end-stage heart failure.
Have a lifeexpectancy of less than 30 days.
Are not eligible for a natural heart transplant.
Have no other viable treatment options
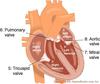
Briefly describe with diagrams the anatomy and working of the heart.
- Has four chambers – Upper two chambers (atria) are holding areas, thin walled – Two pumping lower chambers (ventricles) pump blood out
- Four non return valves – Two valves on either side
- Right side pumps through the lungs (pulmonary circulation)
- Left side pumps through the entire body (systemic circulation)
- Left heart & its valves are more susceptible to damage, since it works against the entire vascular resistance of systemic circulation
State and describe two devices that are used for the management of congestive heart failure.
A ventricular assist device (VAD) is a mechanical pump that’s used to support heart function and blood flow in people who have weakened hearts.
Left Ventricular Assist Device is a surgically implanted mechanical device that helps the heart pump blood
intra aortic balloon pump- IABP


