FINAL REVIEW- EYES, EARS, and RESP system Flashcards
(74 cards)
Geimsa stained smear from ear of a dog; This is….

Malassezia
Most common fungal organism in the ear
bottle-shaped yeast
You can also see Malassezia in the skin, causes dry lesions
In horses guttural pouch mycoses occur as a complication of
Strangles because all of lymphnodes in the retopharyneal region are inflammed, so it blocks the area and fungal organisms can get in
This would probably be aspergilis
Identify the yeast.

Blastomyces
Broad-based budding
Identifiy the yeast.

Histoplasma
these are the smallest and they are usually intracytoplasmic

Cryptococcus
Which of the following bacteria is not generally involved in shipping fever pnuemonia in cattle?
A. Mannhemimia hemolytica
B. Pasteurella multocida
C. Histophilus somni
D. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
D.
shipping fever is mutlifactorial and it almost always involves those three organisms
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
A. Foal pneumonia is caused by Rhodovoccus equi.
B. R. equi is a facultative intracellular bacteria
C. R. equi is partially acid fast
D. Penicillin is the antibiotic of choice in treatming R. equi infections
D penicillin is not affective because it’s intracellular
You want to use macrolides or rhampapin
Moraxella bovis
Infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis in cattle

Moraxella bovis
When will moraxella bovis be the largest problem?
What are the vectors?
IN THE SUMMER
FLIES
this is a very contagious and painful conditiona and it can damage the eyes
Infectious ovine keratoconjunctivitis
Mycoplasma conjunctivae Chlamydia pecorum
Otitis in calves can be caused by
Otitis in calves can be caused by Mycoplasma bovis and Histophilus somni
Ear infections dogs
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Pseudomonas aeruginosa - MOST PROBAMATIC ORGANISM if you treat this then you will probably cover all of these because it’s very hard to treatment because it is resistant to most antiboditics
Escherichia coli
Proteus mirabilis
Malassezia pachydermatis
Are bacteria and fungus usually the primary cause of ear infections?
NO!!!- Bacteria and fungus are secondary causes
How do we diagnosis ear infections?
Diagnosis:
Cytology or Gram staining to examine bacterial and yeast overgrowth
Culture; Samples should be taken with a sterile culturette swab from the horizontal canal or from the middle ear in cases of tympanic rupture.
Address the predisposing/ Primary causes”
Antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy
What is the most common predisposing factor for otitis externa?
ANATOMY- because they have a vertical and then horizontal canal
Conjunctivitis in cats
Chlamydia felis (Feline pneumonitis) - most common
Mycoplasma felis (mycoplasma conjunctivitis)
What are some systemic bacterial infections?
Systemic bacterial infections
Rickettsia,
Anaplasma,
Ehrlichia Brucellosis
Leptospirosis- might be in equine recurrent uvetits
What are some systemic fungal infections in the eye?
Systemic mycoses
Blastomycosis
Cryptococcosis
Histoplasmosis
Coccidioidomycosis
(Protothecosis- fungal like organism; algea)

Chlamydia
You can tell because of the inclusion bodies
Mycotic keratitis in equines
( Aspergillus sp).
common because of the trauma in the eye and they can get secondary keratitis
Equine recurrent uveitis
Equine recurrent uveitis
(Periodic ophthalmia, Moon blindness)
Leptospira infection?/ Immune complex disease?
Iris and uvea are affected
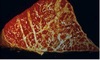
Guttural pouch mycosis
Guttural pouch mycosis
Occurs as complication of Streptococcus equi subsp equi Aspergillus sp
Main complication;nose bleeding (epistaxis) because of the location to the caroid artery; it ruptures
Which hosts are respiratory systems diseases most common in?
FOOD ANIMAL