FINAL SKIN REVIEW Flashcards
(64 cards)
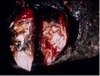
Which of the following conditions you will investigate in a dog presented with this picture?

Staphylococcal pyoderma
food allergy
immune mediated skin conditions
parasitic infections
neoplasm
Dermatitis in bacteriology is often called
pyoderma
Panniculitis
subcutaneous tissue
Cellulitis
dermis and Subcutaneous fat
Most pyoderma/skin infection are due to
Coagulase positive staph
Are skin infections usually the primary issue?
No! Usually problems with the skin are secondary!
Therefore…….
Always investigate underlying causes such as allergy, ectoparasites, Immunosuppressive conditions”
What is the most common gram negative organism that can be involved with a pyoderma skin lesion?
Pseudomonas
A common bacterial isolate from canine pyoderma is
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Fungal differentials
- Actinomycosis- gram positive
- Nocardiosis- gram positive
- Mycobacteriosis- gram positive
What is the diagnostic workup for skin conditions?
- Skin scrapings to rule-out parasites such as Demodex
- Fungal culture to rule-out deep fungal infection
- Skin cytology by performing an impression smear of pustules, papules, crusts or draining tract fluid:
- Bacterial culture / susceptibility testing using fresh purulent discharge or a tissue
- Skin biopsy for dermatohistopathology
What is the treatment?
Systemic antibiotics based on culture and susceptibility (up to 8 weeks or longer in refractory cases)
Fluoroquinolones(broad spectrum): (tissue penetration, Activity against Gram positives and negatives, uptake by macrophages increases penetration and concentration)
Clindamycin (consider inducible clindamycin resistance- macrolide restisttant ) Antibacterial topical therapy (Chlorhexidine)

Inducible clindamycin resistance
All staphylococcus isolates which are macrolide(erythromycin) resistant should be considered Clindamycin resistant unless otherwise confirmed by a D-test
How should you submit a superficial lesion?
Superficial lesions- A culturette swab in transport media
What should you submit for an abscess
Abscess –Fine needle aspirates or contents in anaerobic
transport media
What should you submit for a granulomatous lesion?
Granulomatous lesions- Sample for Biopsy and a fresh piece of tissue for culture
What is recommended for a non-resolving lesion?
For any non-resolving lesions a biopsy is always recommended
Can you submit a dry swab for culture?
Do not submit dry swabs for cultures
Anaerobic infections
Foul smelling discharge, necrotic gangrenous tissue and abscess formation, free gas in tissue, black discoloration of exudates,Sulphur granules in discharge
What do you have to do to take an aerobic culture?
Disinfect skin surface with 70% alcohol, allow to dry
Aspirate specimen directly into the syringe.
Remove air from syringe.
Aseptically transfer material into an anaerobic transport media
Greasy pig disease is caused by
Staphylococcus hyicus
Hemophilius parasuis causes
gram negative
causes blue ears in pigs
GLASSER”S DISEASE
Bumble Foot in birds
Staphylococcus aureus
Botryomycosis-
Botryomycosis- Rodents, Human, Horses Chronic pyogranulomatous inflammation
Most common isolate : S. aureus
deep in the tissue
Wound infections, draining tracts, Abscess
What are your top bacterias that you are considering?
Gram Positive anaerobes
Clostridium
Nocardia
Actinomyces
Gram Negative Anaerobes
Fusobacterium
Bacteroides
Dichelobacter