Gross anatomy and histology of the Female reproductive tract Flashcards
(33 cards)
Function of female preprodutive system?
- Egg production
- Facilitating reproduction with the right conditions
- Production of sex hormones
Vagina is a muscular tube that faciliates mesntruation, child birth and sexual intercourse. The uterus actually protrudes into the vagina, leaving a recess around the uterus in the vagina itself. What is this called?
Vaginal fornix

State the main functions of the uterus
- Hosts the fetus during development
- produces secretions
- allows sperm passage
Cervix is a component of the uterus that extends into vagina. Extends from the ????? of the uterus, to the ???????
The portion that extends into the vagins is called the ?????? portion. The portion that does not extend into the vagina is called?????
Isthmus
External ons - external orifice
Vaginal portion
Supravaginal portion

The internal orifice is opening into the ???? of the uterus, which is connecting the body and the ?????. The regio between the internal ons and external ons is called what?
Cervical canal

The body of the uterus is also known as what? What are two important events happen here?
The corpus.
Fertilization, fetal development
What is the base, or most superior part of the uterus?

The Uterus is composed of 3 layers - name them and very briefly summarise what they are (deep to superficial)
- Endometrium - the mucosa
- Myometrium - muscular layer
- Perimetrium
The endometrium is the innemost layer of uterus - also called uterine mucous membrane.
What type of cell lines the endometrium?
Simple columnar epithelium - underneath you have your typical lamina propria.
Myometrium is a layer of 3 smooth muscle muscle layers.
Subvascular layer
Vascular layer
Supravascular layer
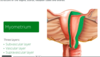
The uterus can be said to be in anteflexion and anteversion. Explain what this means
- Anteversion refers to the position of the uterus to the vagina - V for V
- Anteflexion refers to position of the uterus to the cervix
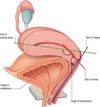
Another name for fallopian tube?
What are the functions of the fallopian tube?
Uterine tube.
Site of fertilisation
Provide passage for ovum

Label the 3 main parts of the fallopian tubes


Describe the appearance of each of the regions of the fallopian tube

Isthmus - narrow sction that connects the ampula to the uterine cavity
Ampulla - widest section of the uterine tube - typically the site of fertilisation
infundibulum - most distal part of fallopian tubes - opening that is near the ovaries to which the fimbrae are attached
Fibrae - finger like, cilitaed projections which capture the ovum from the surface of the ovary
The fallopian tubes connect the uterine cavity to the perionteal cavity. What is the name of the junction that connects the uterus to the fallopian tube?
Utero-tubal junction

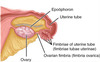
the longest of the fimbriae – ??????? – attaches to the superior aspect of each ovary.
Ovarian fimbriae
Ovaries are bilateral oval shaped discs; that have both exocrine and endocrine activities.
What ligament attaches the uterus body to the sacrum?
Uterosacral ligament
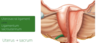
What ligament attaches the ovary to the uterine body?
- The ovarian ligament
What ligament attaches the ovary to the wall of the pelvis?
Suspensory ligament (fold of peritoneum)

What is the function of the broad ligament of the uterus?
- Double layer of peritoneum that connects the uterus to floor and walls of the pelvis
The broad ligament can be divided into roughly 3 areas - what are they?
Mesovarium
Mesoalpinx
Mesometrium
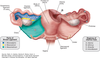
State the functions of each of the 3 parts of the broad ligaments
Mesometrium - surrounds the uterus and is the largest subsection of broad ligament. Runs laterally to cover the external iliac vessels, forming a distinct fold over them.
Mesosalpinx - Originates superiorly to the mesovarium. Encloses the fallopian tubes.
Mesovarium - Encloses the neurovascular supply of the ovary. Also attaches the ovaries to the posterior layer of the mesometrium and encloses the ovarian ligament.

State the structures you would find within the broad ligament
Ovarian artery
Ovarian Vein
What is the part of the uterine tube still enveloped by the uterus?
“Uterine part” of the uterine tube