Hematology Flashcards
(89 cards)
What does high WBC and High PMN’s tell you?
- Stress demargination
- (Stress response - post trauma)
What does a high WBC and <5% Blasts tell you?
- Leukemoid reaction - seen in burn patients or any extreme stress
- (extreme demargination looks like Leukemia)
- Metamyelocytes => Myelocytes
What does high WBC and Bands tell you?
Left shift - they have an infection
What does high WBC and >5% Blasts tell you?
Leukemia
What does high WBC and B Cells tell you?
Bacterial infection
What diseases have high eosinophils?
- “NAACP”
- N - Neoplasm (Lymphoma)
- A - Allergy/ Asthma
- A - Addison’s disease (no cortisol -relative eosinophilia)
- C - Collagen Vascular disease
- P - Parasites
What diseases have high Monocytes (>15%)?
- “STELS”
- Syphilis: chancre, rash, warts
- TB: Hemoptysis, night sweats
- EBV: Teen sick for a month
- Listeria: Sick baby
- Salmonella: Food poisoning
What do high Retics (>1%) tell you?
RBC is being destroyed peripherally

What do low Retics tell you?
Decreased production of bone marrow - not working right

What is Poikilocytosis?
RBC’s of different shapes

What is Anisocytosis?
RBC’s with different sizes

What is the RBC normal lifespan?
120 days
What is the RBC lifespan when there is a problem?
60-90 days (same time as the shelf life of blood bank units)
What is the Platelet lifespan?
7 days
What does “Penia” tell you?
Low Levels - (Usually due to virus or drugs)
What does “Cytosis” tell you?
High levels
What does “Cythemia” tell you?
High levels
What is the difference between Plasma and Serum?
- Plasma: No RBC’s
- Serum: No RBC’s or Fibrinogen
What are the Microcytic Hypochromic Anemias?
- Defect in Hb synthesis (RBC small and pale) “FAST lead”
- F - Fe Deficiency
- A - Anemia of Chronic Disease
- S - Sideroblastic Anemia
- T - Alpha and Beta Thalassemia’s
- L - Lead poisoning
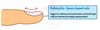
What will you see with Iron Deficiency Anemia?
- Increased TIBC
- associated with
- menses
- GI bleeding
- and Koilonychia
What will you see with Anemia of Chronic Disease?
Decreased TIBC
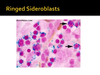
What will you see with Sideroblastic Anemia?
- Decreased dALA synthase
- common with blood transfusions
What will you see with Alpha Thalassemia?
- Seen in African Americans and Asian Americans
- (Chromosome 16- deletion)
What will you see in Beta Thalassemia?
- Seen in Mediterranean’s
- (chromosome 11- point mutation)