Histology: Connective Tissue Flashcards
(37 cards)
1
Q
Define connective tissue.
A
- Supports and connects other tissues and cells to form organs
- Composed of cells and extracellular matrix (ECM)
2
Q
Extracellular Matrix
A
-
Main component of connective tissue
- Protein fibers (collagen, elastic and reticular fibers)
- Ground substance
- Amorphous component (gel-like)
- Binds cells and fibers
3
Q
Protein Fibers: Collagen

A
- Family of proteins
- Most abundant protein in the body (Type I, not heavily glycosylated)
- Major component of CT proper
- Resists shearing and tearing
- Various structures
Image:
- Type I collagen stains eosinophilic (light pink)
- Elastic Fibers (dark pink)
4
Q
Collagen Fibrils LM

A
- Stain pink with acidic dyes (eosinophilic)
- Dark pink are nuclei of fibroblasts
5
Q
Collagen Fibrils EM

A
- Banding pattern
- Reflects arrangment of collagel to form fibrils (next card)
6
Q
Collagen Synthesis
A
- Made by rough ER of fibroblasts
- Procollagen alpha-chains produced (distinctive repeating sequence of Gly-X-Y; glycine usually in the third position)
- Proline and Lysine residues are hydroxylated (requires Vitamin C)
- Procollagen chains assemble into triple helix
- Stabilized by hydrogen bonds between hydroxyprolines
- Packaged into secretory vesicles in Golgi and exocytosed
- Non-helical ends cleaved to form collagen molecule (tropocollagen) outside of the cell
- Triple helix collagen molecules self-assemble into fibrils with staggered arrangment (67 nm banding pattern)
- Results in fibril
- Fibrils are bundled together to form fibers (seen in LM)
- Requires covalent cross-linking (Cu as cofactor)
7
Q
Scurvy
A
-
Vitamin C deficiency
- Results in defective collagen synthesis
- Characterized by:
- Pain/fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Bleeding gums and tooth loss
8
Q
Reticular Fibers

A
- Type III collagen fibrils
- Form branching network
- Requires special stain (PAS, silver stains)
- Because Type III is heavily glycosylated (will not show on H&E)
- Major components in lymphatic and hemopoietic tissues
9
Q
Elastic Fibers

A
- Allows tissues to stretch and return to original shape
- Often interwoven with collagen fibers
- Can form fibers or fenestrated sheets (lamellae)
- Requires special staining for LM (Fuchsin)
Image:
- Blackish strands
10
Q
Elastic Fiber Formation

A
- Scaffold of fibrillin microfibrils (secreted by fibroblasts or smooth muscle)
- Elastin protein deposited onto scaffold
- Elastin cross-links to form, elastin core
Image:
- Just scaffold on left; dark black is elastin deposit and core
11
Q
Ground Substance
A
- Mixture of hydrophilic macromolecules
- Fills spaces between cells and fibers
- Allows diffusion of small molecules
- Barrier to invading substances
3 Main Molecules:
- Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
- Proteoglycans
- Multiadhesive glycoproteins
- Fibronectin
12
Q
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
A
- Polymers of repeating disaccharide units
- When attached to core protein, form proteoglycans
- Usually sulfated
- Synthesized in Golgi
- Attract water to extracellular matrix (gel-like consistency)
13
Q
Hyaluronan (Hyaluronic Acid)
A
- Largest, most ubiquitous GAG
- Synthesized directly in ECM
- Exists as long, free carbohydrate chain
- Link to proteoglycans to form proteoglycan aggregates
- Binds water (responsible for changes in permeability and viscosity within CT)
14
Q
Proteoglycans
A
- Core protein bound to sulfated GAGs
- Produced in rough ER of fibroblasts; secreted by exocytosis
- Bind to hyaluronan after secretion
15
Q
Multiadhesive Glycoproteins
A
- Stabilize the ECM and link to cell surfaces
- Large molceules with branched oligosaccharide chains
- Examples:
- Laminin in basement membrane
- Fibronectin
16
Q
Fibroblasts

A
- Most common cell type in CT
- Elongated cells with oval nuclei
- Difficult to discern cytoplasm
- Produce components of ECM
17
Q
Fibrocytes

A
- Inactive fibroblasts (arrows)
- Heterochromatic nucleus
18
Q
Macrophages

A
- Phagocytic cells (removal of dead cells, tissue debris)
- Derived from monocytes
- Common in loose connective tissue
- Hard to distinguish: eccentric nucleus
- Easier if recently ingested something (inclusions)
19
Q
Macrophage EM

A
- Finger-like projections of cell surface
- Many lysosomes
20
Q
Monocytes
A
- Provide defense by ingesting bacteria
- Participate in immune response (Antigen Presenting Cells)
- Inflammatory response
21
Q
Mast Cells

A
- Derived from hemopoietic stem cells
- Mediate allergic reactions and anaphylactic shock
- Has receptors for IgE
- Abundant basophilic granules
- Granules contain inflammatory response mediators
22
Q
Plasma Cells

A
- Derived from B lymphocytes
- Produce antibodies
- Eccentric nucleus, “clockface nucleus”
- Alternating heterochromatin and euchromatin
23
Q
Mesenchyme
A
-
Loose Embryonic CT
- Most adult CT derived from this form
24
Q
Mucoid CT

A
- Embryonic CT
- Principle component of fetal umbilical cord
- Gelatin-like ground subtance (Wharton’s Jelly)
- Lots of hyaluronan
25
Loose (areolar) CT
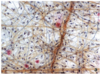
* Loose arrangment of collagen and elastic fibers, embedded in ground substance
* Many cells present:
* Fibroblasts
* Mast Cells
* Macrophages
* **Beneath epithelia**
* **Fills spaces between fibers of muscles and nerves**
* **Most abundant type of CT in the body**
26
Dense CT
* Fewer cells than loose CT
* **Mostly fibroblasts**
* **Abundance of type I collagen in ECM**
* Little ground substance
27
Dense **irregular CT**
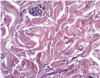
* Collagen fibers **randomly arranged**
* Resistance to stress in **all directions**
* Seen in dermis of skin
28
Dense **regular CT**

* Collagen fibers and fibroblasts arranged in parallel
* Resistance to stress in **one direction**
* Tendons, Ligaments
29
Reticular Connective Tissue

* Loose, located in lymphatic and hematopoietic tissues
* Reticular fibers (**type III collagen**)
Cells:
* **Reticular cells** (specialized fibroblasts)
* Immune cells
30
Adipose Tissue
* Specialized for **energy storage**
* Most of tissue made of **adipocytes** (minimal ECM)
* Other Functions:
* Thermal insulation
* Cushioning to organs
* Shape to body surface
* Cushions areas of mechanical stress (palms, heels)
31
White Adipose Tissue

* Long-term energy storage
* **Single** lipid droplet (**unilocular**)
* Ring-like appearance (nucleus/organelles pushed to side)
* Cells surrounded by external lamina
32
Brown Adipose Tissue

* Specialized to **produce heat**
* ****Abundant mitochondria
* Rich vasculature
* Commonly found in newborns/young children
* **Multiple** lipid droplets (**multilocular**)
33
What types of collagen are not principally produced by fibroblasts?
* **Type II Collagen**
* ****Produced by chondrocytes
* _Predominant collagen in cartilage_
* **Type IV Collagen**
* ****Produced by epithelial cells
* _Found in basal laminae of basement membranes_
* **Most other types of collagen (types I, III, V) are produced by fibroblasts**
34
Where is **type I** collagen found most predominately?
* Bones
* Endomysium of skeletal muscle
* Tendons
* Dermis of Skin
## Footnote
**Most common type of collagen within the body**
35
What type of collagen is hyaline cartilage primarily composed of?
* **Type II**
36
**Matrix Metalloproteinases**
* Class of enzymes are **responsible for degradation of ECM proteins, allowing for turnover and renewal (such as collagen fibers)**
37
Eosinophils
* Bi-lobed nucleus with eosinophilic cytoplam (pink) filled with secretory granules


