Host Barriers Flashcards
(26 cards)
Physical anatomical barriers
Skin and Mucosa
Skin: physical/mechanical barrier
- Closely connected cells with cross-linked keratin 2. High turnover rate 3. Prevents evaporation
Skin: chemical agents
Antimicrobial agents 1. Cathelicidins 2. Defensins 3. Dermicidin Acidic pH
Skin: normal flora
Commensals; do no harm, sometimes benefit
Langerhans cells, derivation, and function
Dendritic cells among keratinocytes Derived from bone marrow Function: APC in immune responses to contact antigens and some skin grafts
Birbeck granules
rod-shaped organelles in Langerhans cells
Mucous membrane organization
- Mucosa
- epithelium
- lamina propria (loose CT w/ glands)
- muscularis mucosae (smooth muscle)
- Submucosa
- dense, irregular CT
- Muscularis externa
- inner/outer smooth muscle
- External layer
- Adventitia (loose CT)
- Serosa (loose CT w/ mesothelial lining)
Four types of intercellular junctions
- Tight junction
- Zona adherens
- Desmosome
- Gap junction
Tight junction
- An occludens junction, composed of claudins and occludins
- Prevents leaking and movement of membrane proteins
Zonula adherens
- An adherens junction, composed of cadherins
- Binds to actin of terminal web (cytoskeleton)
Desmosome
- An adherens junction composed of desmoplakins and plakoglobins
Gap junction
- A communicating junction composed of connexins
Hemidesmosome
- An adherens junction, connects the cell to the basement membrane
Intercellular junction image
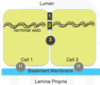
- tight junction
- zona adherens
- desmosome
H. hemidesmosome
Mucosal immunity in Intestine
- Epithelial products
- acidic pH, pancreatic enzymes, bile, intestinal secretions, mucus
- Antimicrobial factors
- lysozyme from Paneth cells in small intestine
- Normal flora
- Lymphoid tissue
Mucosal Immunity in Intestine: Antigen process
- antigens in gut lumen are bound by M cells and undergo transcytosis into their intraepithelial pockets
- dendritic cells take up antigen, process it, present to helper t-cells
- B lymphocytes stimulated to differentiate into plasma cells -> secrete IgA
- IgA transported to gut lumen, binds to antigen on microorganism curface, neutralize
Mucosal immunity in oral cavity
- Epithelium
- physical barrier
- langerhans cells & lymphocytes
- Lamina propria
- macrophages and dendritic cells (Ag uptake by dendrites)
Pemphigus vulgaris
- Acantholytic disorder in persons 30-60, can be fatal
- Formation of severe intraepidermal bullae starting in oral cavity and spreading to skin
- Autoimmune attack of desmosomes
Bullous pemphigoid
- Resembles pemphigus vulgaris but is much less severe
- Subepidermal bullae with inflammatory infiltrate of eosinophils
- Autoimmune attack of hemidesmosomes
Two forms of diffuse lymphoid tissue
- Loose clusters of lymphoid cells
- Lymphoid nodules
Located in mucosa
MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) categories
- GALT = gut-associated lymphoid tissue
- BALT = bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (includes trachea)
- NALT = nose-associated lymphoid tissue
- VALT = vulvovaginal lymphoid tissue
Peyer’s patch
aggregated lymphoid nodules found in the ileum
Respiratory tract host barriers
- Mucus clearance
- secretion of mucins and proteins + water + beating cilia + sneezing/coughing (sometimes)
- Protective antimicrobial factors
- antioxidants
- defensins
- lactoferrins
- lysozymes
Vagina host barriers
- epithelium secretes glycogen
- normal flora convert glycogen to lactic acid –> acidic environment
- antimicrobial factors (biochemical barrier)


