intro to bone biology Flashcards
literally not fucking die (90 cards)
What is paleopathology?
Study of ancient diseases & the reconstruction of past human health & activity patterns
what is a primary source of evidence for paleopathology?
human remains
>mineralized bone
>mummified tissue
>fossilized poop
whats a secondary source of evidence for paleopathology?
texts & art
>texts discussing diseases
>anatomical images

besides human remains, text, and art, what’s another source of evidence for discussing paleopathology?
molecular evidence
>ancient DNA (aDNA)
What is trauma?
injury to bone from an outside (extrinsic) source

what are metabolic disorders?
nutritional problems.

what is scurvy?
a metabolic disorder.
Vitamin C deficiency characterized by excessive bleeding & irregular bone growth.
layers of new bone growing on the normal bone surface

what is rickets?
a metabolic disorder.
vitamin D deficiency that causes a softening/weakening of the bones; poor mineralization of bones
Infectious diseases
caused by pathogenic organisms that live in/on our bodies

what is periostitis?
Infectious disease -> joint disease.
can be acquired as a result of trauma; overuse of the periostium

What are joint diseases?
breakdown of cartilage.
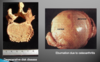
What is osteomyelitis?
infectious disease -> joint disease
infection of the bone from the inside; can occur when a bone breaks and bacteria enters the system.

what are congenital diseases?
diseases you’re born with

What is hydrocephalus?
excess fluid in the brain which can put pressure on the brain & cause the skull to swell; causing damage

What is achondroplasia
genetic bone growth disorder where cartilage doesn’t convert into bone, causing dwarfism

What qualifies as dental disease?
caries (attrition)
enamel hypoplasia

what are caries?
cavities; decaying of tooth

What is enamel hypoplasia?
seen in childhood; thin enamel making teeth vulnerable to decay

give an example of a human cultural practice that alters bone appearance
modern human had their cranium intentionally deformed in childhood.
>when the human was an infant, they bound its head so that it could only grow posteriorly
chinese foot binding
>sign of wealth
what is epidemiology?
the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations, and the application of this study to control health problems
deals with the incidence, distribution, and possible control of diseases and other factors relating to health
what is paleoepidemiology?
use of epidemiological methods & models to understand disease processes, and their impact on ancient populations
What is Mortuis vivis praecipiant?
A term meant to justify what we do with the deceased: Let the dead teach the living.
Dead people teach us how to protect patterns in disease – we wouldn’t know anything about anatomy if it wasnt for dead ppl; how to understand anatomy & decomposition

Why do we care about diseases of the past?
- Helps us understand the history of our diseases & the risk factors for them
- We have genes in our genome that shouldn’t be there – but are there because they help cut certain infectious diseases we’ve been exposed to.
- Altered dead version of diseases we have a history of, in order to use as a basis of vaccines