Intro to Derm (Marsella) Flashcards
(40 cards)
Important aspects of patient history
- Onset
- Length of time of disease
- Seasonality
- Relatives
- Zoonosis
- Environment
- Health status (med hx)
- Life style
- Diet
Primary lesions
- Macule
- Papule
- Plaque
- Pustule
- Vesicle
- Bulla
- Nodule
- Wheal
- Tumor
Macule
Area of skin altered in color, but NOT elevated (patch if > 1 cm diameter)
(primary lesion)

Papule
Solid, raised lesion that has distinct borders (< 1 cm in diameter)
(primary lesion)

Plaque
Elevated lesion w/ flattened top (> 10mm in size)
(primary lesion)

Pustule
Elevations filled w/ pus. Folicular or non-follicular.
(Primary lesion)

Follicular vs. Non-follicular pustules
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- +/- acantholytic cells
- +/- bacteria
Vesicles
Small, clear fluid-filled blisters (< 1mm diameter)
(Primary lesion)

Pustules common with?
Bacterial infections and other inflammatory skin diseases
Vesicles seen with?
Acute contact dermatitis and some autoimmune diseases
Bulla
Clear fluid-filled blister (> 10mm diameter)
(Primary lesion)

Nodule
Firm lesions that extend into the dermis or subcutaneous tissue
(Primary lesion)

Tumor
Swelling or enlargement. May be neoplastic.
(primary lesion)

Wheal
AKA hive. Sharply circumscribed skin elevation produced by edema of the superficial dermis.
(Primary lesion)

Wheals common with?
Allergic reactions
Secondary lesions
- Epidermal collarettes
- Scale
- Crust
- Scar
- Ulcer
- Excoriation
- Lichenification
- Hyperpigmentation
- Hyperkeratosis
Epidermal collarettes
A circular lesion with a circular rim of scale and/or peeling edge. Developed from pastules.
(secondary lesion)

Scale
Flake of abnormal or compacted epithelial cells
(secondary lesion)
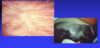
Crust
Dried exudate (containing leukocytes and commonly bacteria)
(secondary lesion)
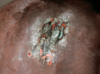
Scar
Fibrotic area resulting from healing of a wound or lesion
(secondary lesion)
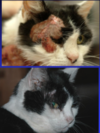
Scarring typically associated with?
Alopecia, depigmentation, and/or thinner dermis
Ulcer
Loss of substance on a cutaneous surface exposing inner layers of tissues. May imply full thickness loss of tissue.
(secondary lesion)
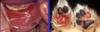
Excoriations
Superficial erosion (usually from scratching or abrasion)
(secondary lesion)
Lichenification
Thickening of the skin secondary to chronic trauma/inflammation.
(secondary lesion)






