L12..2 Pharynx and Soft Palate Flashcards
(21 cards)
Where does the pharynx begin and end
- Begins at base of skull → lower border of cricoid cartilage (C6)
3 different pharynx and the general function?
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
- Closes the POS aspect of nose mouth and larynx → allowing air to go down these areas
Pharyngobasilar fascia
- Where Muscles are deficient SUP → able to see pharyngobasilar fascia
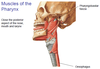
Constrictor muscles of the pharynx: S/M/I constrictors
- SUP: Attaches along raphe on top of buccinator → Projects POS, meets the other constrcitor at midline
- MID: surface of hyoid bone → projects POS into midline, meet with other constrictor at raphe
- INF → Laminar of thyroid cartilage and cricoid cartilage → project POS, meet other constrictor at raphe
- NS from branches of vagus above

Constrictor muscles of the pharynx: Cricopharyngeus
- INF part of the INF constrictor muscles (hard to separate)
- NS from branches of vagus from below
- These constrictor muscles form a sling at the back of these cavities.
- Push food down oral cavity to oesophagus
Internal layer of muscles
- Salpingopharyngeus
- Palatopharyngeus
- Stylopharyngeus
Muscles directed down → when contract → widens pharynx during swallowing
Salpingopharyngeus
Nasopharyngeal tube (auditory tube) to mucular wall of pharynx
Palatopharyngeus
Soft palate to pharynx
Stylopharyngeus
Styloid to pharynx
Penetrates gap b//w SUP and INF constrictors
Nasopharynx
- Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids): If inflammed = difficulty breathing
- Opening of auditory tube below the tubal elevation (formed by cartilaginous auditory tube)
- Opening of tube is important for equilisation of pressure
- If there is a difference b/w pressure inside and out → tympanic membrane may rupture
Salpingopharyngeus unblocking auditory tube
- Salpingopharyngeus attaches to the cartilaginous part of auditory tube
- When it contracts → able to open up auditory tube
- Allow pressure to escape and unblock ear
Oropharynx
- Soft palate and Uvula hanging from the top
- POS 1/3 of tongue
- Have lingual tonsills
- Palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arch

Vallecula
- Space b/w POS 1/3 of tongue and epiglottis → Vallecula
- Food sits at vallecula before pushing epiglottis down and moves into oesophagus
- Protects the largyngeal inlet (which leads into the airway)
Laryngopharynx
- Mucous membrane over cricoid cartilage
- Aryepiglottis fold forms borders of laryngeal inlet
- Epiglottis does not form a perfect seal closing the laryngeal inlet
- Larynx is also elevated and helps form a seal when swallowing
- Piriform recess
- Fluid able to spill out and around laryngeal inlet through piriform recess

Sensory NS of the pharynx
- All by glossopharyngeal N (CN9)
- Forms the afferent arc of Gag reflex
- Use gag reflex to test integrity of glossopharyngeal N
- Forms the afferent arc of Gag reflex
- Except:
- Nasal cavity bits → by branches of trigeminal N
- Some laryngopharynx → some by vagus N
Motor NS of the pharynx
- All by vagus
- Except for: Stylopharyngeus
- Which is by glossopharyngeal N (CN9)
- Vagus N forms the efferent arch of the gag reflex
Soft palate
- Musculus uvulae
- Attached to the hard palate by palatine aponeurosis
- Seal off nasal cavity when coughing
- Seal off oral cavity when chewing (allow breathing when chewing)
- Helps produce suction → close off nasal cavity during sucking
5 muscular support of the soft palate
- Palatoglossus & palatopharyngeus → depress uvula
- Tensor veli palatini: Attaches to LAT part of palatine aponeurosis
- Levator veli palatini
- Both from side of soft palate from above → pulls soft palate up
- Musculus uvulae
- All innervated by pharyngeal branches of vagus; EXCEPT for tensor veli palatini (by Trigeminal)

What are Fauces?
Space bound by palato arches
Waldeyer’s ring
- Incomplete ring of lymphoid tissue that guards the pharynx
- Adenoid + palatine + lingual + tubal tonsils
- A first line defence → more important in children
3 phases of the swallowing reflex
- Bolus shaped and pushed by tongue to palate.
- Soft palate descends and palatal arches are approximated to grip and push the bolus into the oropharynx.
- Soft palate elevated and tightened to prevent bolus entering nasal cavity.
- Larynx and pharynx elevated to bring bolus closer to oesophagus.
- Laryngeal inlet closed to prevent bolus from entering the trachea.
- Bolus is pushed down the oropharynx and over the epiglottis.
- Bolus forced down through laryngopharynx and into oesophagus.
- Larynx depressed to return to normal position (mainly by elastic recoil).


