L1.3 Lungs, pleura, bronchial tree Flashcards
(22 cards)
1
Q
Branches of airway:
1) Trachea
A
- starts lower border of cricoid cartilage → to T4/5 where it bifucates (at the plane of Louis)
- ‘U’ shape cartilaginous ridge (deficient POS)
- POS deficiency bridged by muscles
- Deficiency allows expansion of airway → prevents collapse

2
Q
2) 2 main bronchi
A
- R → shorter & wider
- Hilum = where bronchi enters lungs
- L enters before divide
- R divides before entering (SUP & INT (divides into middle & lower))

3
Q
3) Lobar bronchi
A
- Each goes to single lobe of lung
- 3R, 2L lobes

4
Q
4) segmental bronchi
A
- 9/10 segments of lungs
5
Q
5) Bronchioles
A
- Cartilaginous support ↓ further distally → changes from bronchi → bronchiole (when cart lost)
- Bronchiole → respiratory bronchiole → alveoli

6
Q
Asthma
A
- involves spasm of S.M ~ lower airways
- No cartilaginous support → collapses → difficult breathing
- Cold air makes asthma worsen → triggers S.M spasm
7
Q
What is the position of weakness in the thoracic area
A
- SUP apertures → expose lungs → position of weakness
8
Q
BS to lungs
A
- Pulmonary blood supply for gas exchange, follows similar branching pattern as airways
- A (carry DeO2) → branches of pul. Trunk ( blood to lungs)
- Hilum position: SUP & POS
- V (carry O2) → blood towards heart
- Hilum position: INF & ANT
- Pressure difference b/w A & V are very small (Thickness difference not as great as other A & V)

9
Q
Bronchial supply to lungs
A
- Supplies parenchyma (non-respiratory parts - i.e not alveoli)
- Derived from bronchial A which is a branch of descending aorta → branches down to smaller levels
10
Q
Venous drainage
A
- Bronchial veins → azygous vein
11
Q
Bronchopulmonary segments
A
- Pyramid shaped with ‘apex’ towards hilum and base on surface
- Supplied by segmental bronchus, A & V
- Functionally distinct
- Surgically resected without disrupting other lung units
12
Q
Structures on the R medial surface
A
- A - SUP & POS
- V - INF & ANT
- 2 lobar bronchi

13
Q
Impressions on the R lung
A
- SVC, R Brachiocephalic V, Azygous, Cardiac impression
14
Q
Structures on the L medial surfcae
A
- Single LMB
- A - SUP
- V - INF & ANT

15
Q
Impressions on the L lung
A
- Arch of aorta, Descending aorta, cardiac impression
16
Q
N supply to the lungs
A
- Parasym: From vagus N (10th cranial N)
- Over arch of aorta → behind LMB → branch to bronchiole tree
- Sym: T1-4
- Synapse at sym ganglia → branches towards bifurcation
- Inhibits S.M around bronchi
17
Q
Lymphatics of the lungs
A
- Vessels → nodes → trunks → Duct (R lymphatic & thoracic) → Vein (Subclavin)
- Deep pul lymphatic vessels
- SUP lymphatic vessels
- Both drain via hilum lymph nodes → tracheal nodes → bronchomediastinal trunk
- Macrophages aggregate in lymph nodes → macrophage presents carbon (may be black in colour as a result)

18
Q
Pleura
A
- Closed, double layer membrane surrounding each lung
- Vis & Parietal
- May have costodiaphragmatic recess in parietal (results in diaphragm moving down)

19
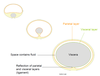
Q
What is the pulmonary ligament
A
- Pulmonary ligament → parietal pleura extended down from hilum
- At the point of reflection → allows structures into lungs
20
Q
Development of the pleura
A
- Coelom → viscera moves in & enlarges → double layer membrane surrounds it
21
Q
N supply to the pleura
A
- Visceral → same sensory N which innervates visceral
- Visceral afferent - T1-4 from sym
- Parietal → from somatic N located adjacent to membrane
- Phrenic, intercostal
22
Q
Importance of surface tension from pleura
A
- important for breathing
- Broken/punctured → lung collapses


